目录
- 一.准备数据
- 创建数据表
- 插入数据
- 二.SQL演练
- 1. SQL语句的强化
- 2. 创建 “商品分类”” 表
- 3. 同步表数据
- 4. 创建 “商品品牌表” 表
- 5. 同步数据
- 6. 修改表结构
- 7. 外键
- 三.数据库的设计
- 创建 “商品分类” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
- 创建 “商品品牌” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
- 创建 “商品” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
- 创建 “顾客” 表
- 创建 “订单” 表
- 创建 “订单详情” 表
- 说明
- 四.Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
- 引入模块
- Connection 对象
- Cursor对象
- 五.增删改查
- 查询一行数据
- 查询多行数据
- 六.参数化
一.准备数据
创建数据表
-- 创建 "京东" 数据库 create database jing_dong charset=utf8; -- 使用 "京东" 数据库 use jing_dong; -- 创建一个商品goods数据表 create table goods( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(150) not null, cate_name varchar(40) not null, brand_name varchar(40) not null, price decimal(10,3) not null default 0, is_show bit not null default 1, is_saleoff bit not null default 0 );
插入数据
-- 向goods表中插入数据 insert into goods values(0,'r510vc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','3399',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'y400n 14.0英寸笔记本电脑','笔记本','联想','4999',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'g150th 15.6英寸游戏本','游戏本','雷神','8499',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'x550cc 15.6英寸笔记本','笔记本','华硕','2799',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'x240 超极本','超级本','联想','4880',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'u330p 13.3英寸超极本','超级本','联想','4299',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'svp13226scb 触控超极本','超级本','索尼','7999',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 7.9英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','1998',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'ipad air 9.7英寸平板电脑','平板电脑','苹果','3388',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'ipad mini 配备 retina 显示屏','平板电脑','苹果','2788',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'ideacentre c340 20英寸一体电脑 ','台式机','联想','3499',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'vostro 3800-r1206 台式电脑','台式机','戴尔','2899',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'imac me086ch/a 21.5英寸一体电脑','台式机','苹果','9188',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'at7-7414lp 台式电脑 linux )','台式机','宏碁','3699',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'z220sff f4f06pa工作站','服务器/工作站','惠普','4288',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'poweredge ii服务器','服务器/工作站','戴尔','5388',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'mac pro专业级台式电脑','服务器/工作站','苹果','28888',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'hmz-t3w 头戴显示设备','笔记本配件','索尼','6999',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'商务双肩背包','笔记本配件','索尼','99',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'x3250 m4机架式服务器','服务器/工作站','ibm','6888',default,default); insert into goods values(0,'商务双肩背包','笔记本配件','索尼','99',default,default);
二.SQL演练
1. SQL语句的强化
查询类型cate_name为 ‘超极本’ 的商品名称、价格
select name,price from goods where cate_name = '超级本';
显示商品的种类
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
求所有电脑产品的平均价格,并且保留两位小数
select round(avg(price),2) as avg_price from goods;
显示每种商品的平均价格
select cate_name,avg(price) from goods group by cate_name;
查询每种类型的商品中 最贵、最便宜、平均价、数量
select cate_name,max(price),min(price),avg(price),count(*) from goods group by cate_name;
查询所有价格大于平均价格的商品,并且按价格降序排序
select id,name,price from goods where price > (select round(avg(price),2) as avg_price from goods) order by price desc;
查询每种类型中最贵的电脑信息
select * from goods inner join ( select cate_name, max(price) as max_price, min(price) as min_price, avg(price) as avg_price, count(*) from goods group by cate_name ) as goods_new_info on goods.cate_name=goods_new_info.cate_name and goods.price=goods_new_info.max_price;
2. 创建 “商品分类”” 表
-- 创建商品分类表 create table if not exists goods_cates( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, name varchar(40) not null );
查询goods表中商品的种类
select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
将分组结果写入到goods_cates数据表
insert into goods_cates (name) select cate_name from goods group by cate_name;
3. 同步表数据
通过goods_cates数据表来更新goods表
update goods as g inner join goods_cates as c on g.cate_name=c.name set g.cate_name=c.id;
4. 创建 “商品品牌表” 表
通过create…select来创建数据表并且同时写入记录,一步到位
-- select brand_name from goods group by brand_name; -- 在创建数据表的时候一起插入数据 -- 注意: 需要对brand_name 用as起别名,否则name字段就没有值 create table goods_brands ( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment, name varchar(40) not null) select brand_name as name from goods group by brand_name;
5. 同步数据
通过goods_brands数据表来更新goods数据表
update goods as g inner join goods_brands as b on g.brand_name=b.name set g.brand_name=b.id;
6. 修改表结构
查看 goods 的数据表结构,会发现 cate_name 和 brand_name对应的类型为 varchar 但是存储的都是数字
desc goods;
通过alter table语句修改表结构
alter table goods change cate_name cate_id int unsigned not null, change brand_name brand_id int unsigned not null;
7. 外键
分别在 goods_cates 和 goods_brands表中插入记录
insert into goods_cates(name) values ('路由器'),('交换机'),('网卡');
insert into goods_brands(name) values ('海尔'),('清华同方'),('神舟');
在 goods 数据表中写入任意记录
insert into goods (name,cate_id,brand_id,price)
values('LaserJet Pro P1606dn 黑白激光打印机', 12, 4,'1849');
查询所有商品的详细信息 (通过内连接)
select g.id,g.name,c.name,b.name,g.price from goods as g inner join goods_cates as c on g.cate_id=c.id inner join goods_brands as b on g.brand_id=b.id;
查询所有商品的详细信息 (通过左连接)
select g.id,g.name,c.name,b.name,g.price from goods as g left join goods_cates as c on g.cate_id=c.id left join goods_brands as b on g.brand_id=b.id;
- 如何防止无效信息的插入,就是可以在插入前判断类型或者品牌名称是否存在呢? 可以使用之前讲过的外键来解决
- 外键约束:对数据的有效性进行验证
- 关键字: foreign key,只有 innodb数据库引擎 支持外键约束
- 对于已经存在的数据表 如何更新外键约束
-- 给brand_id 添加外键约束成功 alter table goods add foreign key (brand_id) references goods_brands(id); -- 给cate_id 添加外键失败 -- 会出现1452错误 -- 错误原因:已经添加了一个不存在的cate_id值12,因此需要先删除 alter table goods add foreign key (cate_id) references goods_cates(id);
- 如何在创建数据表的时候就设置外键约束呢?
- 注意: goods 中的 cate_id 的类型一定要和 goods_cates 表中的 id 类型一致
create table goods( id int primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) default '', price decimal(5,2), cate_id int unsigned, brand_id int unsigned, is_show bit default 1, is_saleoff bit default 0, foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(id), foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(id) );
如何取消外键约束
-- 需要先获取外键约束名称,该名称系统会自动生成,可以通过查看表创建语句来获取名称 show create table goods; -- 获取名称之后就可以根据名称来删除外键约束 alter table goods drop foreign key 外键名称;
在实际开发中,很少会使用到外键约束,会极大的降低表更新的效率
三.数据库的设计
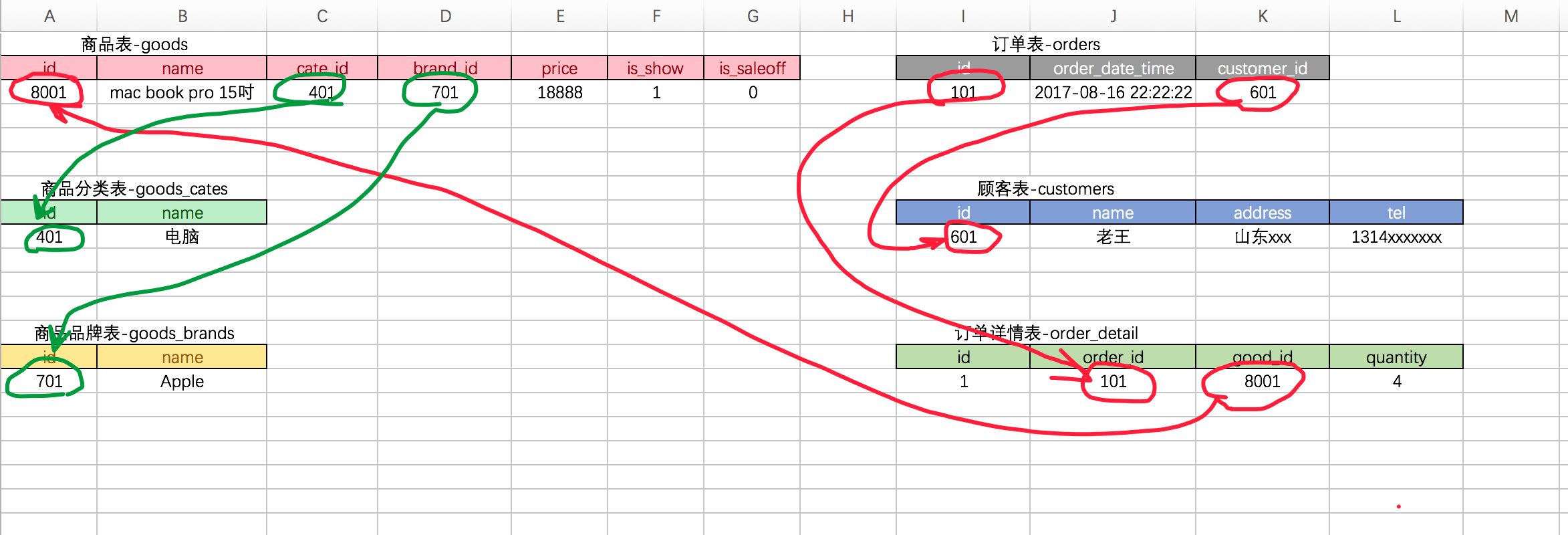
创建 “商品分类” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
create table goods_cates( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) not null );
创建 “商品品牌” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
create table goods_brands ( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) not null );
创建 “商品” 表(之前已经创建,无需再次创建)
create table goods( id int unsigned primary key auto_increment not null, name varchar(40) default '', price decimal(5,2), cate_id int unsigned, brand_id int unsigned, is_show bit default 1, is_saleoff bit default 0, foreign key(cate_id) references goods_cates(id), foreign key(brand_id) references goods_brands(id) );
创建 “顾客” 表
create table customer( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, name varchar(30) not null, addr varchar(100), tel varchar(11) not null );
创建 “订单” 表
create table orders( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, order_date_time datetime not null, customer_id int unsigned, foreign key(customer_id) references customer(id) );
创建 “订单详情” 表
create table order_detail( id int unsigned auto_increment primary key not null, order_id int unsigned not null, goods_id int unsigned not null, quantity tinyint unsigned not null, foreign key(order_id) references orders(id), foreign key(goods_id) references goods(id) );
说明
- 以上创建表的顺序是有要求的,即如果goods表中的外键约束用的是goods_cates或者是goods_brands,那么就应该先创建这2个表,否则创建goods会失败
- 创建外键时,一定要注意类型要相同,否则失败
四.Python 中操作 MySQL 步骤
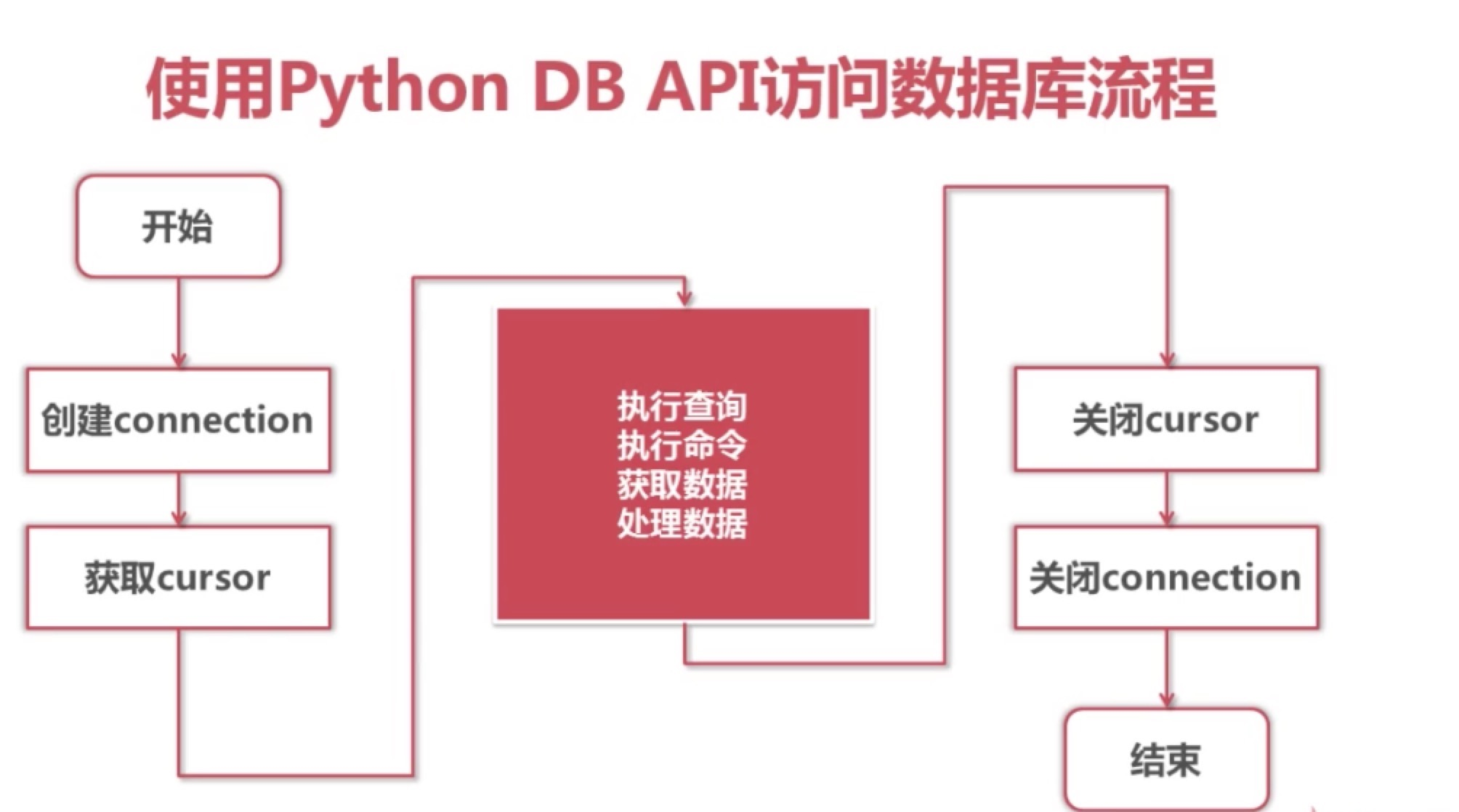
引入模块
在py文件中引入pymysql模块
from pymysql import *
Connection 对象
- 用于建立与数据库的连接
- 创建对象:调用connect()方法
conn=connect(参数列表)
- 参数host:连接的mysql主机,如果本机是’localhost’
- 参数port:连接的mysql主机的端口,默认是3306
- 参数database:数据库的名称
- 参数user:连接的用户名
- 参数password:连接的密码
- 参数charset:通信采用的编码方式,推荐使用utf8
对象的方法
- close()关闭连接
- commit()提交
- cursor()返回Cursor对象,用于执行sql语句并获得结果
Cursor对象
- 用于执行sql语句,使用频度最高的语句为select、insert、update、delete
- 获取Cursor对象:调用Connection对象的cursor()方法
cs1=conn.cursor()
对象的方法
- close()关闭
- execute(operation [, parameters ])执行语句,返回受影响的行数,主要用于执行insert、update、delete语句,也可以执行create、alter、drop等语句
- fetchone()执行查询语句时,获取查询结果集的第一个行数据,返回一个元组
- fetchall()执行查询时,获取结果集的所有行,一行构成一个元组,再将这些元组装入一个元组返回
对象的属性
- rowcount只读属性,表示最近一次execute()执行后受影响的行数
- connection获得当前连接对象
五.增删改查
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,database='jing_dong',user='root',password='mysql',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行insert语句,并返回受影响的行数:添加一条数据
# 增加
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("硬盘")')
#打印受影响的行数
print(count)
count = cs1.execute('insert into goods_cates(name) values("光盘")')
print(count)
# # 更新
# count = cs1.execute('update goods_cates set name="机械硬盘" where name="硬盘"')
# # 删除
# count = cs1.execute('delete from goods_cates where id=6')
# 提交之前的操作,如果之前已经之执行过多次的execute,那么就都进行提交
conn.commit()
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
查询一行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
for i in range(count):
# 获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchone()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 获取查询的结果
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
查询多行数据
from pymysql import *
def main():
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询一条数据
count = cs1.execute('select id,name from goods where id>=4')
# 打印受影响的行数
print("查询到%d条数据:" % count)
# for i in range(count):
# # 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
# # 打印查询的结果
# print(result)
# # 获取查询的结果
result = cs1.fetchall()
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
六.参数化
- sql语句的参数化,可以有效防止sql注入
- 注意:此处不同于python的字符串格式化,全部使用%s占位
from pymysql import *
def main():
find_name = input("请输入物品名称:")
# 创建Connection连接
conn = connect(host='localhost',port=3306,user='root',password='mysql',database='jing_dong',charset='utf8')
# 获得Cursor对象
cs1 = conn.cursor()
# # 非安全的方式
# # 输入 " or 1=1 or " (双引号也要输入)
# sql = 'select * from goods where name="%s"' % find_name
# print("""sql===>%s<====""" % sql)
# # 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
# count = cs1.execute(sql)
# 安全的方式
# 构造参数列表
params = [find_name]
# 执行select语句,并返回受影响的行数:查询所有数据
count = cs1.execute('select * from goods where name=%s', params)
# 注意:
# 如果要是有多个参数,需要进行参数化
# 那么params = [数值1, 数值2....],此时sql语句中有多个%s即可
# 打印受影响的行数
print(count)
# 获取查询的结果
# result = cs1.fetchone()
result = cs1.fetchall()
# 打印查询的结果
print(result)
# 关闭Cursor对象
cs1.close()
# 关闭Connection对象
conn.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
以上就是MySQL和Python交互的示例的详细内容,更多关于MySQL和python交互的资料请关注NICE源码其它相关文章!








