前言
分享两个监测元素是否在视口内的方法
1. 位置计算
使用 Element.getBoundingClientRect() 方法返回元素相对于视口的位置
const isElementVisible = (el) => {
const rect = el.getBoundingClientRect();
};
获取浏览器窗口的宽高
const isElementVisible = (el) => {
const rect = el.getBoundingClientRect();
const vWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth;
const vHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight;
};
判断元素是否在视口内,如图所示
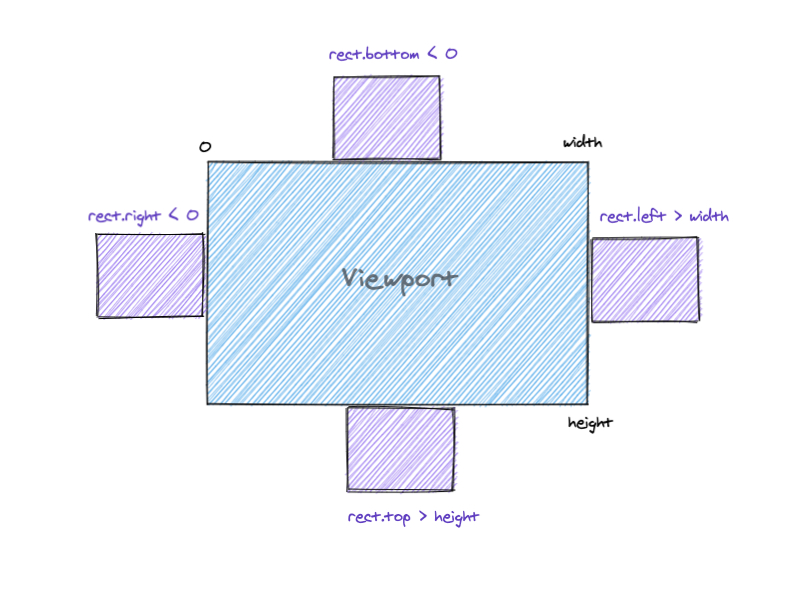
const isElementVisible = (el) => {
const rect = el.getBoundingClientRect()
const vWidth = window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth
const vHeight = window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight
if (
rect.right < 0 ||
rect.bottom < 0 ||
rect.left > vWidth ||
rect.top > vHeight
) {
return false
}
return true
}
getBoundingClientRect 方法会使浏览器发生回流和重绘,性能消耗稍大,但兼容性比 Intersection Observer 要好。
2. Intersection Observer
The Intersection Observer API provides a way to asynchronously observe changes in the intersection of a target element with an ancestor element or with a top-level document’s viewport.
Intersection Observer API提供了一种异步检测目标元素与祖先元素或 viewport 相交情况变化的方法。在目标元素与视口或者其他指定元素发生交集时和触发配置的回调函数。
// 获取要监测的元素
const boxes = document.querySelectorAll('.box')
// 创建观察者,配置回调函数
// 通过 isIntersecting 属性判断元素与视口是否相交
const observer = new IntersectionObserver((entries, observer) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
console.log(
entry.target,
entry.isIntersecting ? "visible" : "invisible"
);
});
})
boxes.forEach((box) => {
observer.observe(box);
});
参考
how-to-check-an-element-is-in-viewport-4bcl
Intersection Observer API
总结
到此这篇关于如何利用JS检查元素是否在视口内的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JS检查元素在视口内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!