目录
- 前言
- 使用
- 组件编写
- 数据结构解析
- 流程解析
- 底层代码解析
- 其他
- 总结
前言
密码强度文件校验器; 注册帐号的时候我们需要对用户当前的密码强度进行一个评估,这个过程我们需要做一个检测器,最好写的灵活点,这样方便产品修改规则。
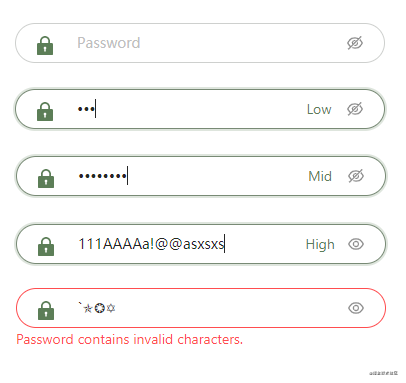
先看下效果吧~~ 下面是截图对应的状态
使用
1 参数传递
const PasswordForce = passwordForce({ inputValue, className: ‘password-force’, });
2 使用
<PasswordForce.View />
3 校验
检测是否超出字符PasswordForce.invaildWord
实现例子
我们配置antd实现下密码输入框上面绑定一个提示器吧
1,2都是不需要改的,但是实际我们需要监听input的值然后设置值。于是我们可以定义一个监听修改value的函数
const [inputValue, setInputValue] = useState('');
const passwordChange = (value: string) => {
setInputValue(value);
};
const onPasswordInput = (e: any) => {
passwordChange(e?.target?.value || '');
};
然后绑定即可,绑定好了我们就可以正常显示了,但是,如果输入了非法字符,这时候我们需要通过拦截器拦截。
<Form.Item
...
rules={[
{
required: true,
message: 'Password not empty',
},
({ getFieldValue }) => ({
validator(_, value) {
passwordChange(value);
if (PasswordForce.invaildWord) {
return Promise.reject(
new Error('Password contains invalid characters.'),
);
}
return Promise.resolve();
},
}),
]}
...
好了,使用片结束,我们实现下吧。
组件编写
编写组件
import {
getRuleMatchResult,
IpasswordForce,
IpasswordRule,
isMatchForceResultConfig,
matchResultConfig,
passwordBreakKey,
} from '@/utils/passwordStrengthChecker';
import React, { CSSProperties } from 'react';
import { useEffect } from 'react';
import { useState } from 'react';
import styled from 'styled-components';
interface props {
inputValue: string;
color?: string;
style?: CSSProperties;
className?: string;
customRule?: IpasswordRule[];
}
enum ForceMap {
high = 'High',
middle = 'Mid',
low = 'Low',
}
const boolNumSum = (list: boolean[]) =>
list.reduce<number>(
(previousValue, currentValue) =>
currentValue ? previousValue + 1 : previousValue,
0,
);
const passwordForce: (props: props) => {
View: React.FC;
invaildWord: boolean;
force: IpasswordForce;
} = ({ inputValue, style = {}, className, customRule = [] }) => {
const [force, setforce] = useState<IpasswordForce>(false);
const [invaildWord, setIsInvaildWord] = useState(false);
const inputValueLen = inputValue?.length || 0;
const setData = () => {
setforce(false);
const isFirstWordUp = inputValue[0] === inputValue[0].toLocaleUpperCase();
const ruleRsult = getRuleMatchResult(customRule, inputValue, undefined, '');
const matchNum = boolNumSum(ruleRsult.list.map((e) => e[passwordBreakKey]));
const matchResultConfig: matchResultConfig[] = [
{ min: 0, max: 32, matchNum: 1, value: 'low' },
{ min: 7, max: 32, matchNum: 2, value: 'middle' },
{ min: 7, max: 32, matchNum: 3, value: 'middle' },
{ min: 15, max: 32, matchNum: 3, value: 'high', need: isFirstWordUp },
];
setIsInvaildWord(ruleRsult.invaildWord);
matchResultConfig.forEach((config) => {
isMatchForceResultConfig(config, matchNum, inputValueLen) &&
setforce(config.value);
});
};
useEffect(() => {
inputValue ? setData() : setforce(false);
}, [inputValue]);
return {
View: () =>
force ? (
<PasswordForceWrap {...{ style, className }}>
{ForceMap[force]}
</PasswordForceWrap>
) : (
<></>
),
invaildWord,
force,
};
};
export default passwordForce;
const PasswordForceWrap = styled.span`
color: ${({ color }) => color ?? '#000'};
`;
数据结构解析
- list 规则的集合,每一个规则都有是否匹配到和规则名及已规则数据本身。
- map 就是方便直接获取对应规则的数据。
- matchCount 就是匹配到的字符数
- invaildWord 可以根据这个来判断是否有非法字符(超过规则本身规定的字符)
流程解析
这个其实就两个流程
- 根据输入的值和规则获取处理后的数据,获得的数据结构如上面所示。
- 然后再编写具体符合业务需求的config数据交给isMatchForceResultConfig函数去匹配设置强度
嗯。 业务代码差不多就这么多了。 然后里面关于依赖那就是属于基本不会改动的代码,基于下面底层的文件,在业务代码我们可以配置出很复杂的校验器,这部分代码我们可以在其他文件上实现。
底层代码解析
让我们来康康吧。
下面是纯ts代码,可以运行任意框架哦。
passwordStrengthChecker.ts
import { numberList, specialList, wordList } from './constants';
type map = <U, T>(opstion: {
array: U[];
range: number;
matchList: T[];
tokenMap: (updateItem: T, token: U, index: number) => T;
breakKey?: string;
arrayMap?: (item: U, index: number) => void;
}) => T[];
/**
* match array and set
*/
export const setArrayMatch: map = ({
array,
range,
matchList,
breakKey,
tokenMap,
arrayMap,
}) => {
const tokenLen = array.length;
for (let tokenIndex = tokenLen - 1; tokenIndex >= 0; tokenIndex--) {
const arrayToken = array[tokenIndex];
arrayMap && arrayMap(arrayToken, tokenIndex);
for (let findIndex = range - 1; findIndex >= 0; findIndex--) {
matchList = matchList.map((item) =>
tokenMap(item, arrayToken, findIndex),
);
}
if (breakKey && !matchList.map((e) => (e as any)[breakKey]).includes(false))
break;
}
return matchList;
};
export const passwordBreakKey = 'isMatch';
export type IpasswordRule = {
list: string[];
isMatch: boolean;
name: string;
};
export const defaultPasswordRuleList = [
{ name: 'special', list: specialList },
{ name: 'num', list: numberList },
{ name: 'word', list: wordList },
];
type PickValue<T, K extends keyof T> = T[K];
export const getRuleMatchResult: (
customRule: IpasswordRule[],
inputValue: string,
disableDefaultRule?: boolean,
breakKey?: string,
) => {
list: IpasswordRule[];
map: Map<PickValue<IpasswordRule, 'name'>, boolean>;
matchCount: number;
invaildWord: boolean;
} = (customRule, inputValue, disableDefaultRule = true, breakKey) => {
let ruleList = [
...(disableDefaultRule ? defaultPasswordRuleList : []),
...customRule,
].map((item) => ({ ...item, [passwordBreakKey]: false }));
const range = Math.max(...ruleList.map((ruleItem) => ruleItem.list.length));
let matchCount = 0;
ruleList = setArrayMatch<string, IpasswordRule>({
array: inputValue.split(''),
range,
matchList: ruleList,
// not breakKey full match
breakKey: breakKey === void 0 ? passwordBreakKey : breakKey,
tokenMap: (ruleItem, inputToken, findIndex) => {
const match = ruleItem?.list[findIndex] === inputToken;
if (match) {
matchCount++;
return { ...ruleItem, isMatch: true };
}
return ruleItem;
},
});
return {
list: ruleList,
map: new Map(ruleList.map((e) => [e.name, e[passwordBreakKey]])),
matchCount,
// 想要获取这个值,必须breakKey设置为空字符,如果提前退出会导致提前中止条件
// To get this value, breakkey must be set to null string
invaildWord: matchCount !== inputValue.length,
};
};
export const isMatchForceResultConfig = (
config: matchResultConfig,
matchNum: number,
inputValueLen: number,
) => {
return (
matchNum === config.matchNum &&
inputValueLen >= config.min &&
inputValueLen <= config.max &&
(config.need !== undefined ? config.need : true)
);
};
export type matchResultConfig = {
min: number;
max: number;
matchNum: number;
value: IpasswordForce;
need?: boolean;
back?: IpasswordForce;
};
export type IpasswordForce = false | 'high' | 'middle' | 'low';
流程就是合并规则,一个是默认规则一个是自定义规则,如果自定义规则,那么就会覆盖默认规则。
从规则中,寻找规则数量最长的规则,因为等下我们遍历的时候可以合并所有的规则,不管多少规则,其实遍历数是区别不大的。
遍历函数是个单独的高阶函数,可以自定义处理内部的逻辑,这时候,我们匹配到了之后对应的规则,激活对应规则的属性,并累计匹配到的字符。
最后正常全部匹配到了就应该中止遍历,但是有一个情况是不能中止的,那就是需要判断是否有非法字符。
最后这个函数把处理过的数据丢给上层组件,流程就是这样
在数据抛出的过程中,有些场景可能需要对对应规则的数据进行特殊处理,但是如果是array结构就很不方便,于是抛出的数据应该分为list和map类型,上层应用想要获取对应规则的情况可以map.get(规则名称)来操作
constants.ts
export const specialList = ["~", "!", "@", "#", "$", "%", "^", "&", "*", "(", ")", "_", "=", "-", "/", ",", ".", "?", "<", ">", ";", ":", "[", "]", "{", "}", "|", "\\"];
export const numberList = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', '0'];
export const wordList = ["q", "a", "z", "w", "s", "x", "e", "d", "c", "r", "f", "v", "t", "g", "b", "y", "h", "n", "u", "j", "m", "i", "k", "o", "l", "p", "Q", "A", "Z", "W", "S", "X", "E", "D", "C", "R", "F", "V", "T", "G", "B", "Y", "H", "N", "U", "J", "M", "I", "K", "O", "L", "P"];
其他
很多人可能会有疑问,一个代码检测器有必要搞这么复杂吗,直接正则不好吗。其实从实用角度来说,确实正则更方便点,但是有时候我们不想要循规蹈矩,或者想要手动编码的快感,或者要从无聊中代码获得更多的可玩性等,于是编写一个看起来挺复杂的代码,不过把底层的封装住,然后保留灵活性,在业务层里面尽量简单点,其实也不是不可以试试的,但是也会在review的时候被怼,各位看官拷贝请注意哈,时间紧迫或者编码能力不强的不建议使用本代码,出问题本人概不负责。
总结
到此这篇关于react如何实现一个密码强度检测器的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关react密码强度检测器内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!