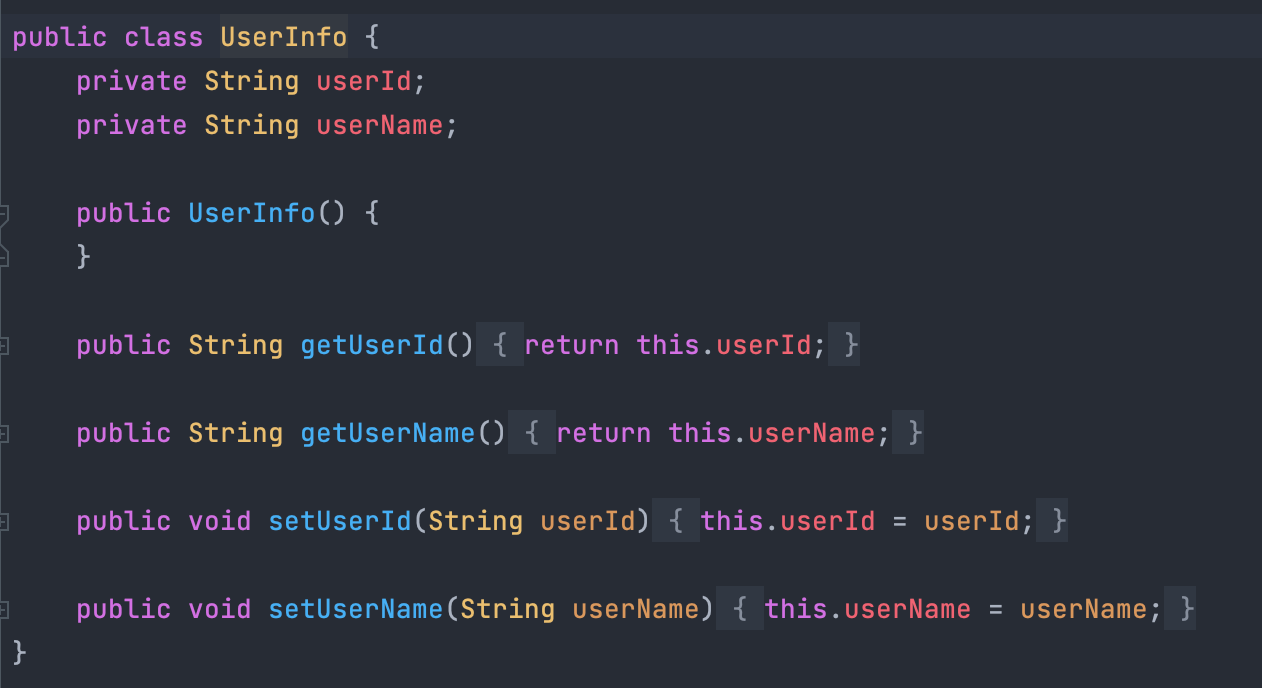
常规方案
使用FileReader以utf-8格式读取文件,根据文件内容是否包含乱码字符�,来判断文件是否为utf-8。
如果存在�,即文件编码非utf-8,反之为utf-8。
代码如下:
const isUtf8 = async (file: File) => {
return await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsText(file);
reader.onloadend = (e: any): void => {
const content = e.target.result;
const encodingRight = content.indexOf("") === -1;
if (encodingRight) {
resolve(encodingRight);
} else {
reject(new Error("编码格式错误,请上传 UTF-8 格式文件"));
}
};
reader.onerror = () => {
reject(new Error("文件内容读取失败,请检查文件是否损坏"));
};
});
};
该方法问题在于,如果文件非常大,比如几个G,浏览器读到的内容直接放在内存中,fileReader实例会直接触发onerror,抛出错误,有时浏览器会直接崩溃。
大文件方案
对于大文件,可以对文件内容进行抽样,对文件进行切片,这里使用100片。对切出的每片文件再切取前面1kb大小的片段,以string方式读取。如果1024B可能正好切在某个汉字编码的中间,导致以string方式读取时出错,即首尾可能出现�,被认为是非utf-8片段。这时可以取1kb对应字符串的前半段,再去判断�是否存在。
上述常数可以根据需求进行调整。
代码如下:
const getSamples = (file: File) => {
const filesize = file.size;
const parts: Blob[] = [];
if (filesize < 50 * 1024 * 1024) {
parts.push(file);
} else {
let total = 100;
const sampleSize = 1024 * 1024;
const chunkSize = Math.floor(filesize / total);
let start = 0;
let end = sampleSize;
while (total > 1) {
parts.push(file.slice(start, end));
start += chunkSize;
end += chunkSize;
total--;
}
}
return parts;
};
const isUtf8 = (filePart: Blob) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const fileReader = new FileReader();
fileReader.readAsText(filePart);
fileReader.onload = (e) => {
const str = e.target?.result as string;
// 大致取一半
const sampleStr = str?.slice(4, 4 + str?.length / 2);
if (sampleStr.indexOf("�") === -1) {
resolve(void 0);
} else {
reject(new Error(编码格式错误,请上传 UTF-8 格式文件"));
}
};
fileReader.onerror = () => {
reject(new Error(文件内容读取失败,请检查文件是否损坏"));
};
});
};
export default async function (file: File) {
const samples = getSamples(file);
let res = true;
for (const filePart of samples) {
try {
await isUtf8(filePart);
} catch (error) {
res = false;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
到此这篇关于js判断文件是否为utf-8编码的方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关js判断utf-8内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!