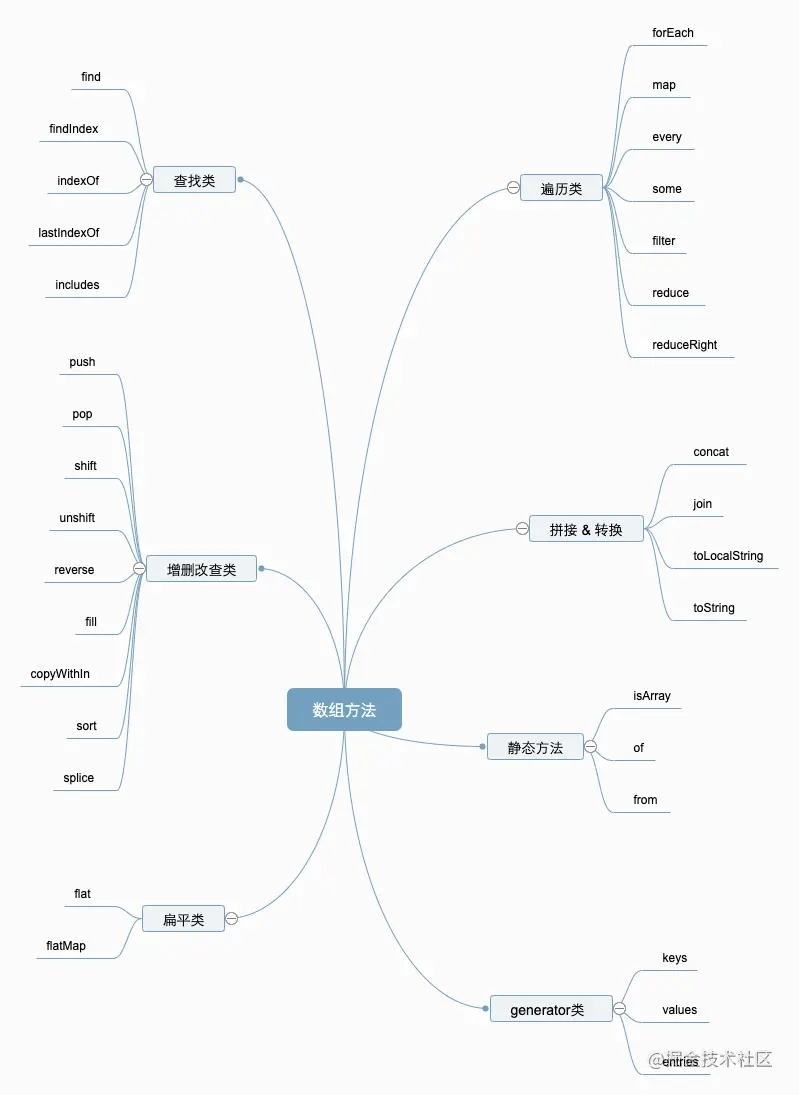
目录
- 方法一:set :不是一种数据类型,是一种数据结构;成员唯一
- 方法二:对象属性名不能重复
- 方法三:indexOf
- 方法四:sort
- 方法五:includes :包含;如果数组包含那一项,返回true;不包含返回false;
- 方法六:hasOwnProperty : 检测属性名是否是对象的一个私有属性;返回一个布尔值;
- 方法七:filter+indexOf
- 方法八:splice
- 方法九:递归
- 方法十:Map :利用了Map数据结构存值的特点;
- 方法十一:reduce
- 方法十二:类似于方法一的set,用了剩余运算符…
还有其他可以处理数组的几个方法~
- includes:方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,根据情况,如果包含则返回 true,否则返回false。
- find:返回第一次找到的那一项
- some:返回一个布尔值,只要一个是true,就返回true
- every:返回一个布尔值,需要每一项都是true,才返回true
- filter:返回一个过滤后的新数组;如果返回true就留下,false就过滤掉
- reduce:收敛
下面我们进入正题~(希望能对你有帮助~小编有点皮!!哈哈哈哈哈哈)
方法一:set :不是一种数据类型,是一种数据结构;成员唯一
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let s = new Set(ary);
// Array.from : 将set数据结构转成真正的数组;
return Array.from(s)
}
unique(arr);
方法二:对象属性名不能重复
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let obj = {};
for(let i=0;i<ary.length;i++){
let cur = ary[i];
if(obj[cur]){
//ary.splice(i,1);// 导致数组塌陷
ary[i]=ary[ary.length-1];
ary.length--;// 删除最后一项
i--;
continue;
}
obj[cur]=cur;// 给obj新增键值对;属性名和属性值是一样的
}
}
unique(arr);
方法三:indexOf
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let newAry = [];
for(let i=0;i<ary.length;i++){
let cur = ary[i];
if(newAry.indexOf(cur)===-1){
newAry.push(cur);
}
}
return newAry;
}
unique(arr)
方法四:sort
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let a = ary.sort(function (a,b) {
return a-b;
});
for(let i=0;i<a.length;i++){
if(a[i]===a[i+1]){
a.splice(i+1,1);
i--;
}
}
return a;
}
unique(arr)
方法五:includes :包含;如果数组包含那一项,返回true;不包含返回false;
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let newAry = [];
let len = ary.length;
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
let cur = ary[i];
if(!newAry.includes(cur)){
newAry.push(cur);
}
}
return newAry;
}
console.log(unique(arr));
方法六:hasOwnProperty : 检测属性名是否是对象的一个私有属性;返回一个布尔值;
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let obj = {};
return ary.filter(function (item,index,a) {
// item : 数组每一个成员
// index: 成员对应的索引
// a : 整个数组
// hasOwnProperty来校验的该属性是否出现过;
return obj.hasOwnProperty(typeof item+item)?false:obj[typeof item+item]=true;
if(obj.hasOwnProperty(typeof item+item)){
return false
}else{
obj[typeof item+item]=true;
return true;
}
})
}
console.log(unique(arr))
方法七:filter+indexOf
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
return ary.filter(function (item,index,a) {
return ary.indexOf(item)===index;
})
}
console.log(unique(arr));
方法八:splice
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
for(let i=0;i<ary.length;i++){
for(j=i+1;j<ary.length;j++){
if(ary[i]===ary[j]){
ary.splice(j,1);
j--;
}
}
}
return ary;
}
unique(arr);
方法九:递归
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let len= ary.length;
ary = ary.sort(function (a,b) {
return a-b;
});
function loop(index) {
if(index>=1){
if(ary[index]===ary[index-1]){
ary.splice(index,1);
}
loop(index-1)
}
}
loop(len-1);
return ary;
}
console.log(unique(arr));
方法十:Map :利用了Map数据结构存值的特点;
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
let newAry =[];
let map = new Map();
for(let i=0;i<ary.length;i++){
if(!map.has(ary[i])){
map.set(ary[i],true);
newAry.push(ary[i]);
}
}
}
unique(arr);
方法十一:reduce
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
function unique(ary) {
// reduce : 第一个是函数,第二个参数会传给第一次回调的prev;
return ary.reduce((prev,next)=>{
// 该函数返回值是下一次执行的prev;
return prev.includes(next)?prev:[...prev,next];
},[])
}
console.log(unique(arr));
方法十二:类似于方法一的set,用了剩余运算符…
let arr = [12,1,12,3,1,88,66,9,66];
let a = [...new Set(arr)];
console.log(a);
到此这篇关于JS数组方案的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关JS数组去重内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!