目录
- vue router
- 1、认识路由的概念
- 1.1、何为路由
- 1.2、后端路由阶段
- 1.3、前端路由阶段
- 1.4、前端渲染和后端渲染?
- 2、前端路由的规则
- 2.1、URL的hash 方式
- 2.2、HTML5的history模式
- 3、route-view的基础
- 3.1 认识vue-router
- 3.2、安装和使用vue-router
- 3.3、路由的默认路径
- 3.4、HTML5的history模式
- 3.5、router-link补充
- 3.6、路由代码跳转
- 3.7、动态路由
- 4、路由的懒加载
- 4.1、认识懒加载
- 4.2、懒加载效果
- 4.3、懒加载方式
- 5、路由的嵌套使用
- 5.1、认识嵌套路由
- 5.2、实现过程
- 5.3、嵌套路由的默认路径
- 6、路由传递参数
- 6.1、准备工作
- 6.2、获取参数
- 6.3、router和route区别
- 7、路由导航守卫
- 8、keep-alive
- 9、TabBar练习
- 9.1、需求表述
- 9.2、需求分析
- 9.3、需求实现
vue router
1、认识路由的概念
1.1、何为路由
通过互联的网络把信息从源地址传输到目的地址的活动.
1.2、后端路由阶段
早期的网站开发整个HTML页面是由服务器来渲染的.
服务器直接生产渲染好对应的HTML页面, 返回给客户端进行展示.
但是, 一个网站, 这么多页面服务器如何处理呢?
一个页面有自己对应的网址, 也就是URL.
URL会发送到服务器, 服务器会通过正则对该URL进行匹配, 并且最后交给一个Controller进行处理.
Controller进行各种处理, 最终生成HTML或者数据, 返回给前端.
这就完成了一个IO操作.
上面的这种操作, 就是后端路由.
当我们页面中需要请求不同的路径内容时, 交给服务器来进行处理, 服务器渲染好整个页面, 并且将页面返回给客户端
这种情况下渲染好的页面, 不需要单独加载任何的js和css, 可以直接交给浏览器展示, 这样也有利于SEO的优化.
后端路由的缺点:
一种情况是整个页面的模块由后端人员来编写和维护的.
另一种情况是前端开发人员如果要开发页面, 需要通过PHP和Java等语言来编写页面代码.
而且通常情况下HTML代码和数据以及对应的逻辑会混在一起, 编写和维护都是非常糟糕的事情.
1.3、前端路由阶段
前后端分离阶段:
随着Ajax的出现, 有了前后端分离的开发模式.
后端只提供API来返回数据, 前端通过Ajax获取数据, 并且可以通过JavaScript将数据渲染到页面中.
这样做最大的优点就是前后端责任的清晰, 后端专注于数据上, 前端专注于交互和可视化上.
并且当移动端(iOS/Android)出现后, 后端不需要进行任何处理, 依然使用之前的一套API即可.
目前很多的网站依然采用这种模式开发.
单页面富应用阶段:
其实SPA最主要的特点就是在前后端分离的基础上加了一层前端路由.
也就是前端来维护一套路由规则.
前端路由的核心是什么呢?
改变URL,但是页面不进行整体的刷新。
如何实现呢?
1.4、前端渲染和后端渲染?
前端渲染:服务器直接生产渲染好对应的HTML页面, 返回给客户端进行展示。比如:jsp页面
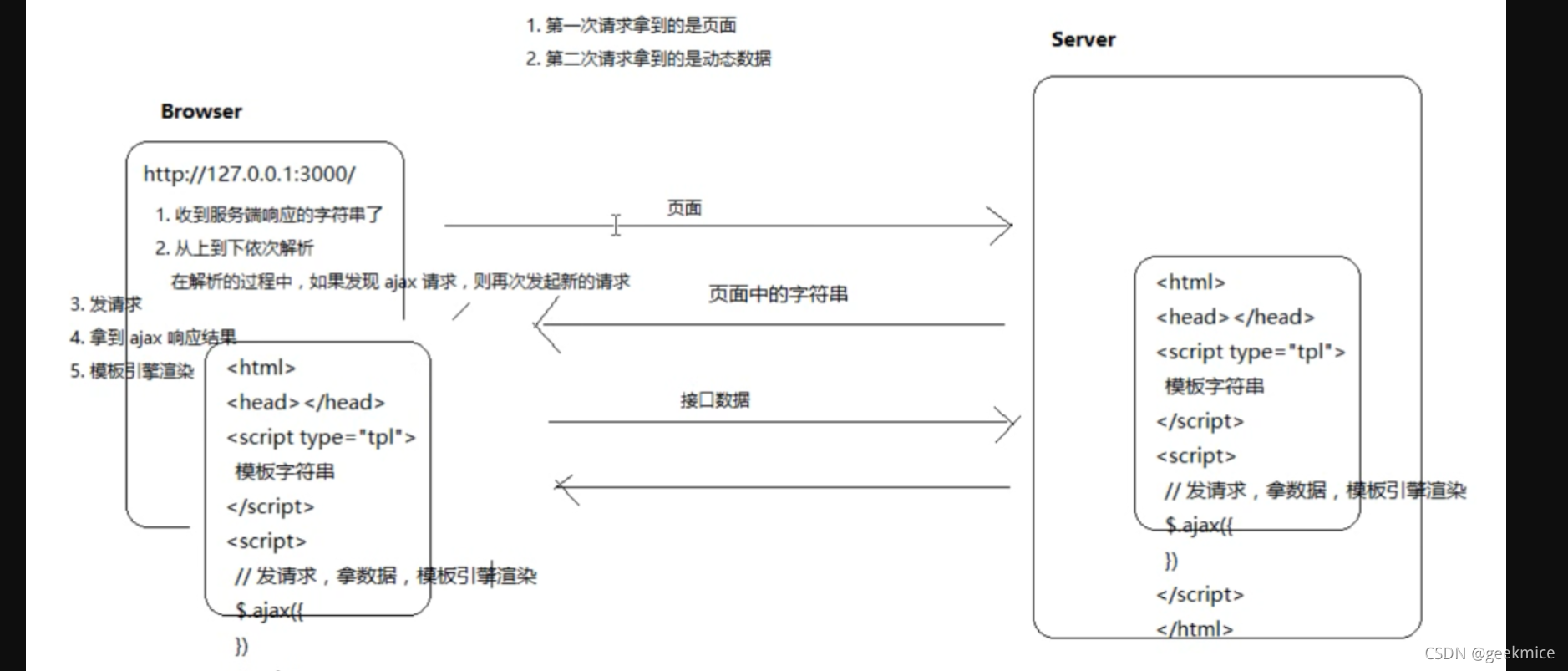
后端渲染:后端返回JSON数据,前端利用预先写的html模板,循环读取JSON数据,拼接字符串,并插入页面。

2、前端路由的规则
2.1、URL的hash 方式
location说明
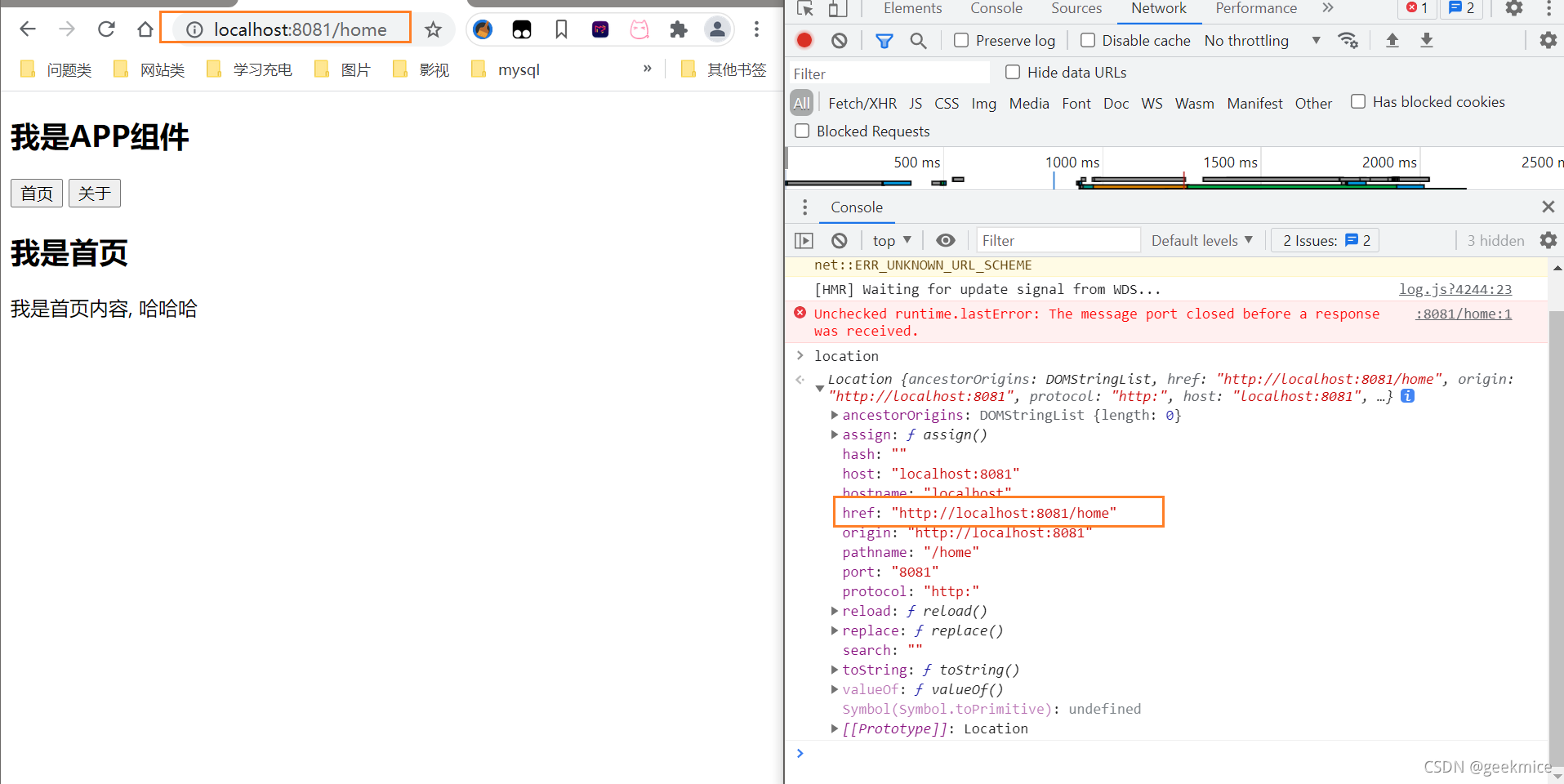
location.href效果 页面整个刷新
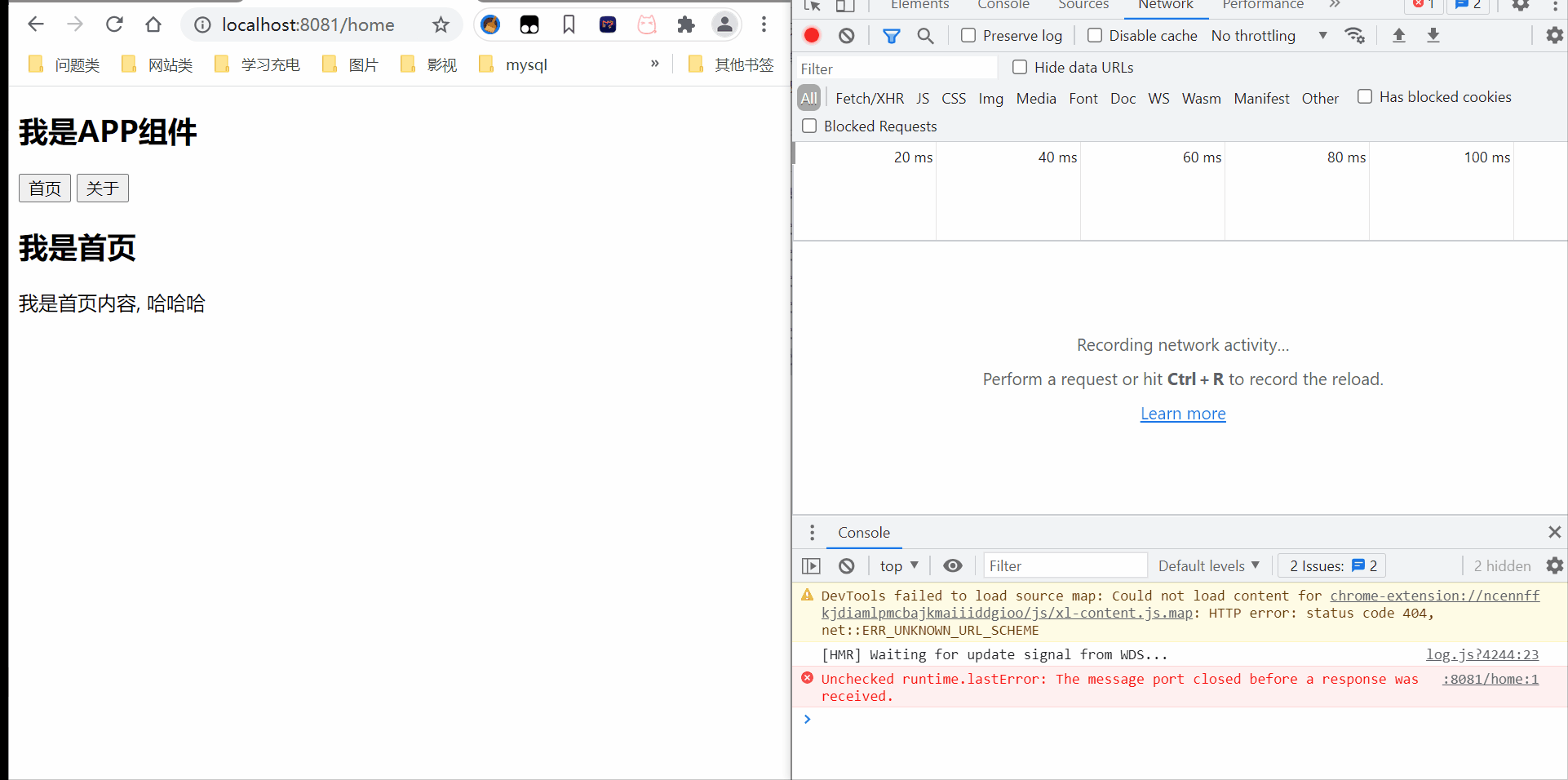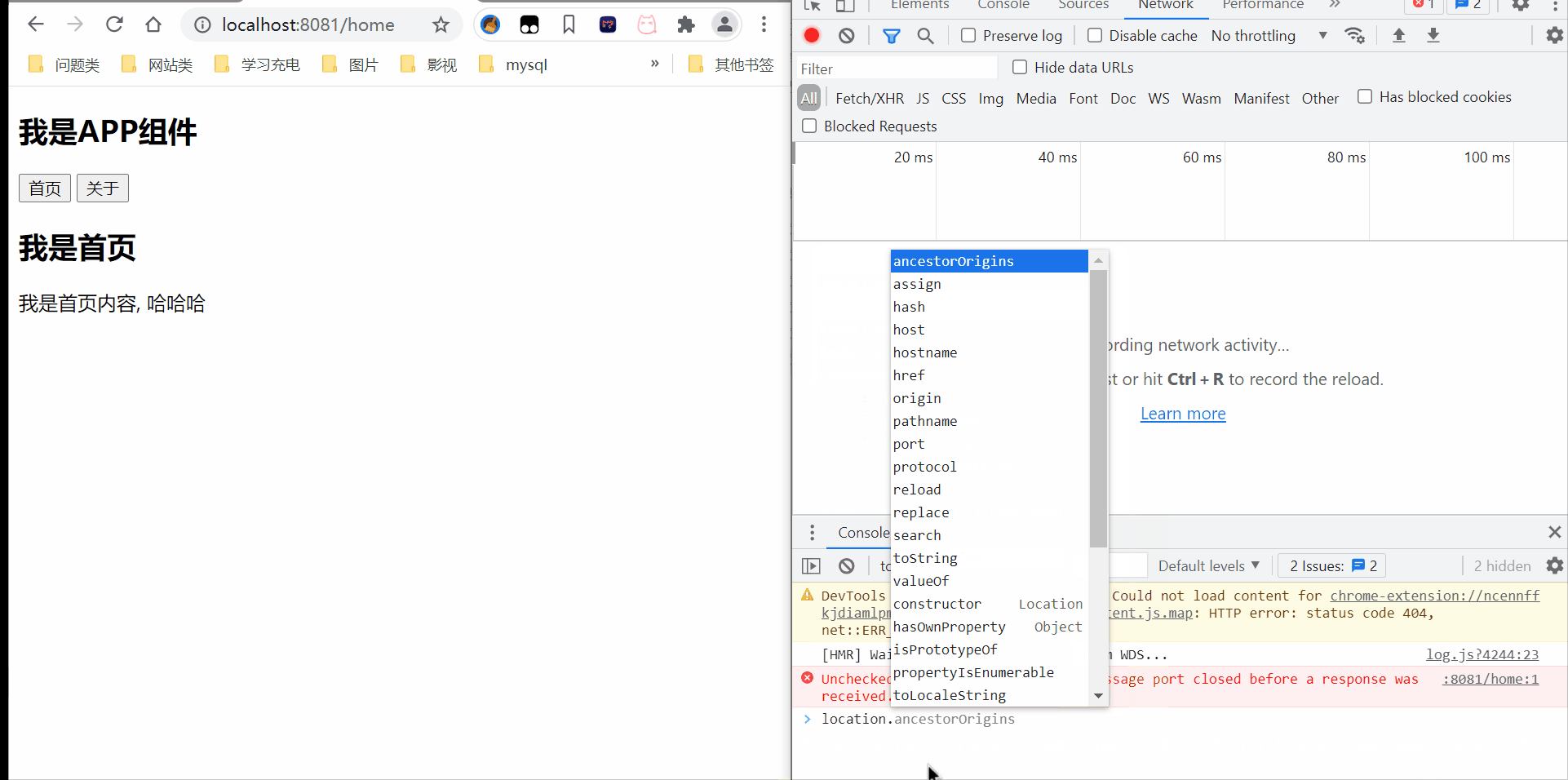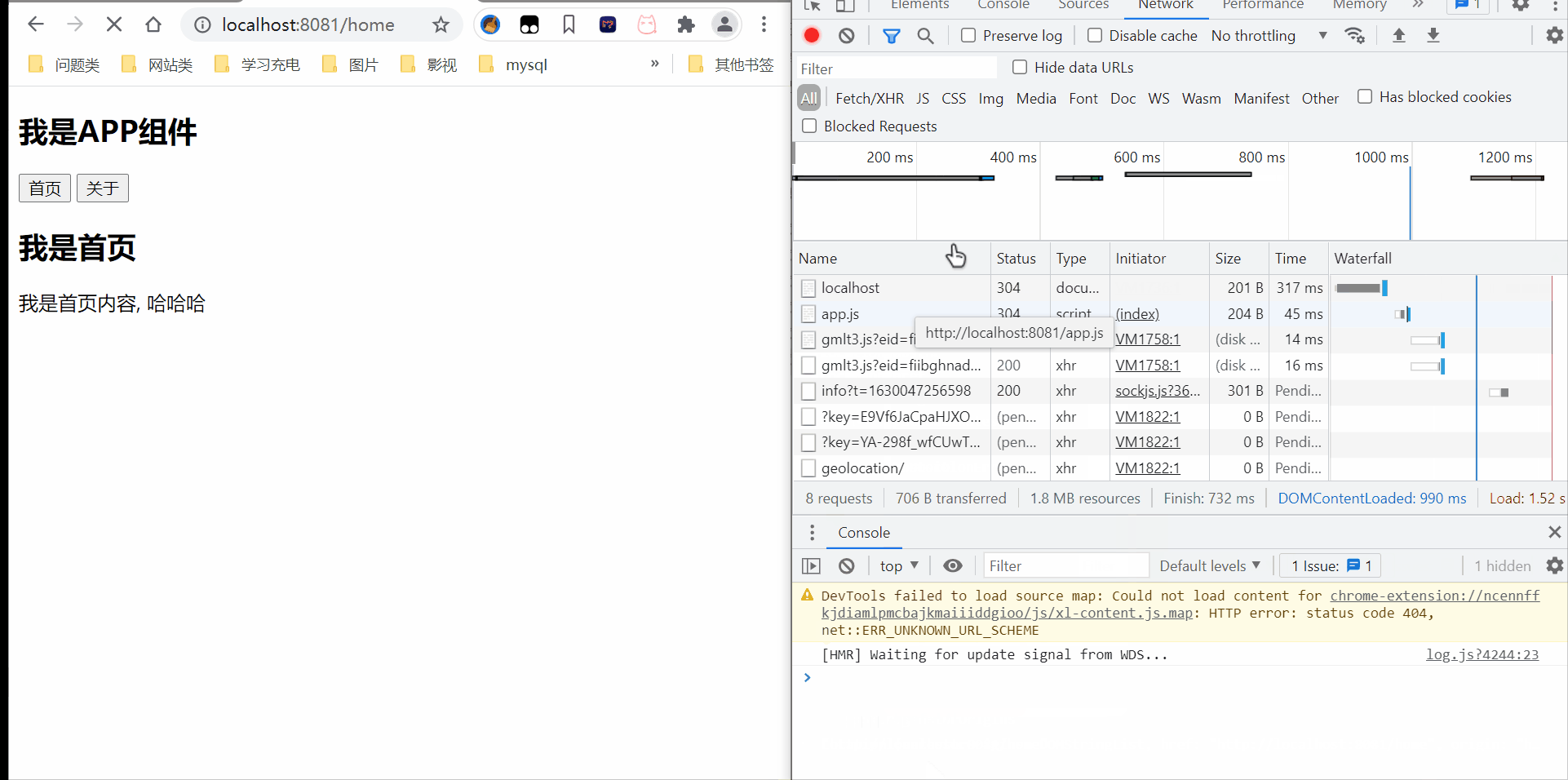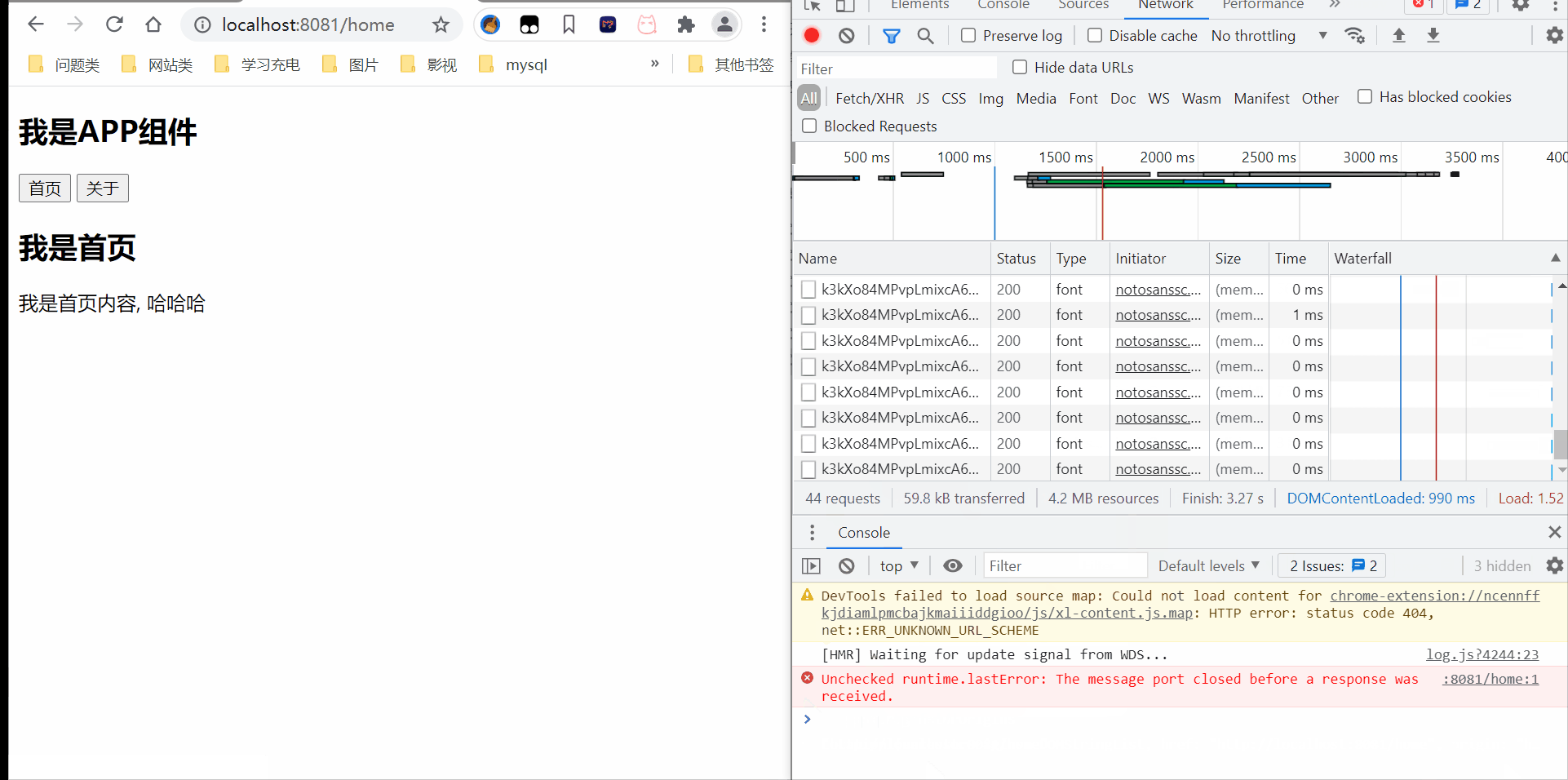
location.hash 局部刷新 而非全部刷新
2.2、HTML5的history模式
- pushState back 栈结构
特点:先进后出 pushState:入栈 back:出栈
效果如下
- replaceState back 替换
不能回退
- go
history.go(-1) 后退一步
history.go(1) <=> history.forward() 前进一步
3、route-view的基础
3.1 认识vue-router
- vue-router是基于组件和路由实现
路由用于设定访问路径, 将路径和组件映射起来.
在vue-router的单页面应用中, 页面的路径的改变就是组件的切换.
3.2、安装和使用vue-router
- 使用webpack创建工程化开发
- 安装npm install vue-router –save
- 模块化使用
导入路由对象,并且调用Vue.use(VueRouter)
创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
在vue实例中挂载创建的路由实例
- 使用vue-router步骤
创建路由组件
配置路由映射,组件和路径映射关系
About.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是关于</h2>
<p>我是关于内容, 呵呵呵</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "About"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
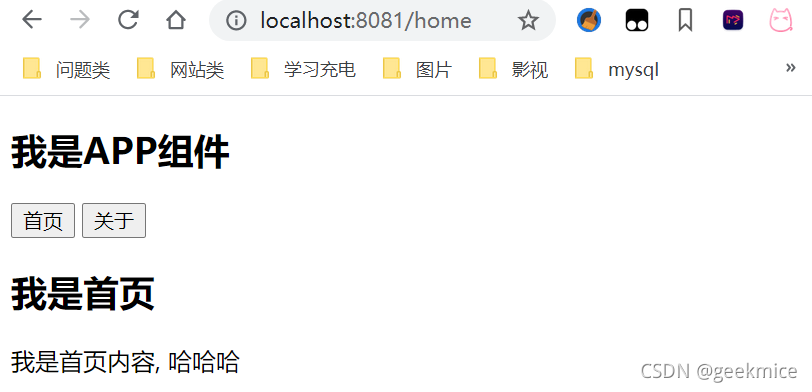
Home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是首页</h2>
<p>我是首页内容, 哈哈哈</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
router -> index.js
// 创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
<!--路由的默认值-->
// 页面默认加载 直接访问主页
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode:"history",
linkActiveClass:"active"
})
- 使用路由 router-link和router-view 显示
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="about">About</router-link>
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
大致流程
1、通过指令创建vue项目
vue create vuerouterstudy
2、删除默认生成的HelloWorld组件相关信息
3、创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
Home.vue
<template>
<div>
我是首页内容
</div>
</template>
index.js
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Vue from 'vue'
import Home from '../components/Home'
// 1、通过Vue.use(插件名) 安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2、创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
}
]
// 3、配置路由和组件之间映射关系
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
// 4、将router对象传入Vue实例
export default router
使用路由
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 渲染超链接 a -->
<router-link to="/home" tag="button">主页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button">关于</router-link>
<!-- 动态渲染组件 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: {},
};
</script>
<style>
</style>
简要说明组件
<router-link>:该标签是一个vue-router已经内置的组件,最终会被渲染一个a链接 <router-view>:该标签会根据当前路径,动态渲染出不同组件 网页的其他内容,比如顶部的标题导航,或者说 底部的一些版权信息和<router-view>处于同一登记 路由切换时候,切换就是<router-view>挂载的组件,其他内容不改变
最终效果图
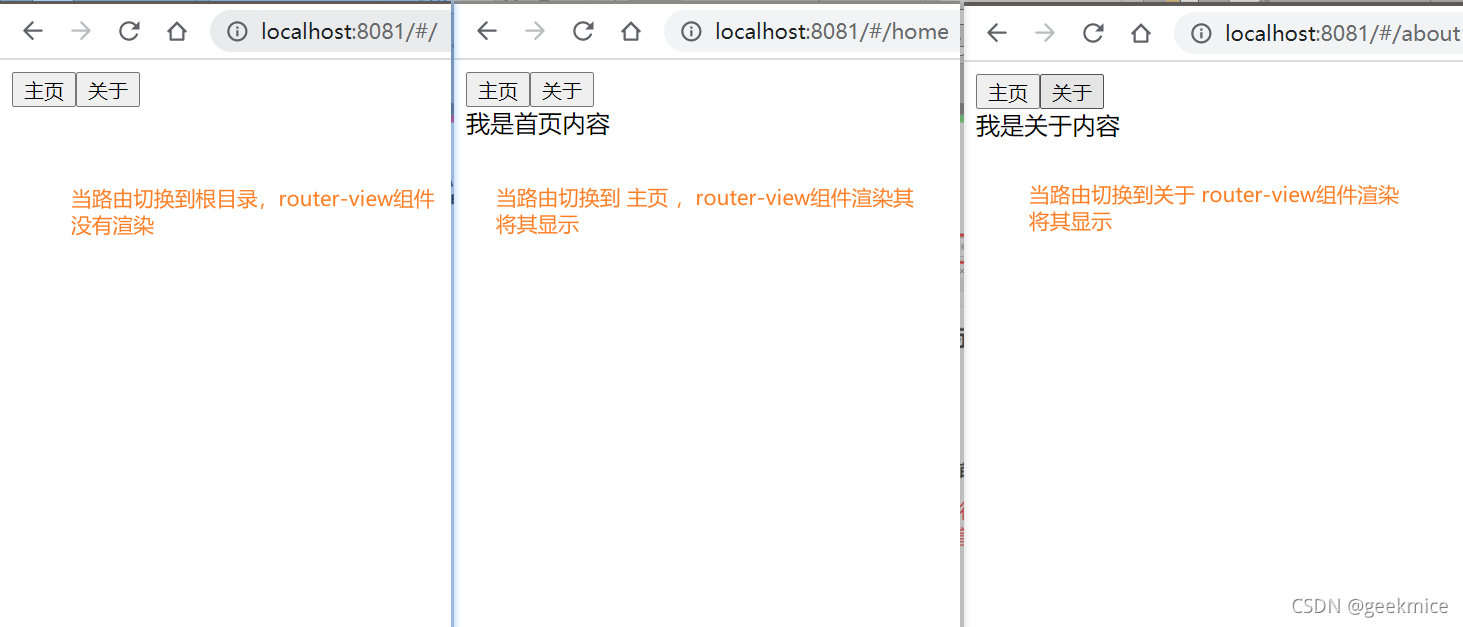
3.3、路由的默认路径
默认情况下, 进入网站的首页, 我们希望<router-view>渲染首页的内容.
但是我们的实现中, 默认没有显示首页组件, 必须让用户点击才可以.
如何可以让路径默认跳到到首页, 并且<router-view>渲染首页组件呢?
非常简单, 我们只需要配置多配置一个映射就可以了.
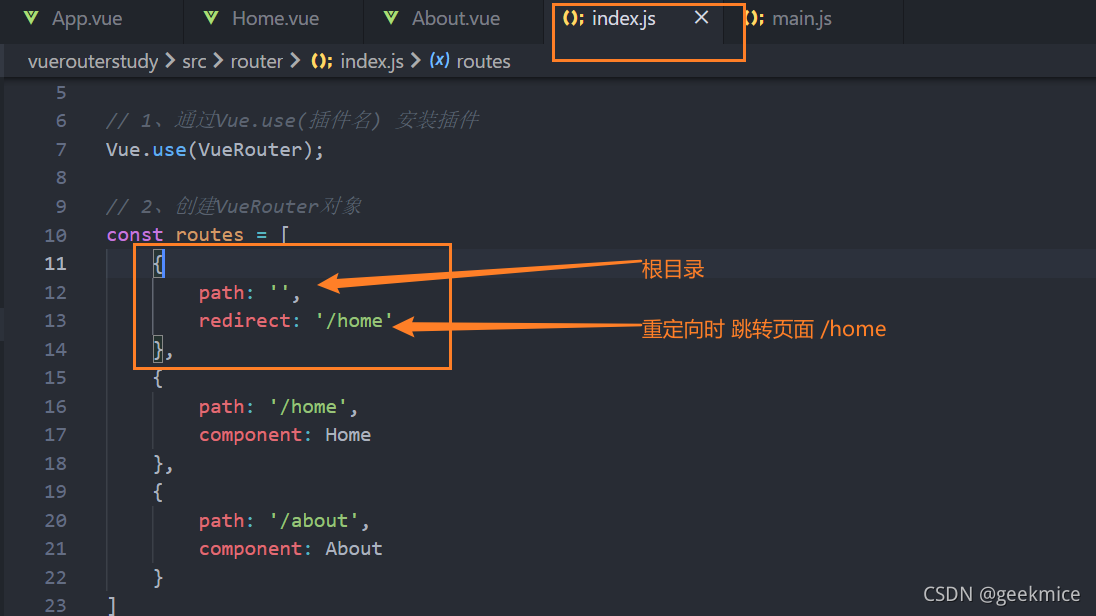
配置解析
我们在routes中又配置了一个映射.
path配置的是根路径: /
redirect是重定向, 也就是我们将根路径重定向到/home的路径下, 这样就可以得到我们想要的结果了.
3.4、HTML5的history模式
页面默认是 url的hash模式
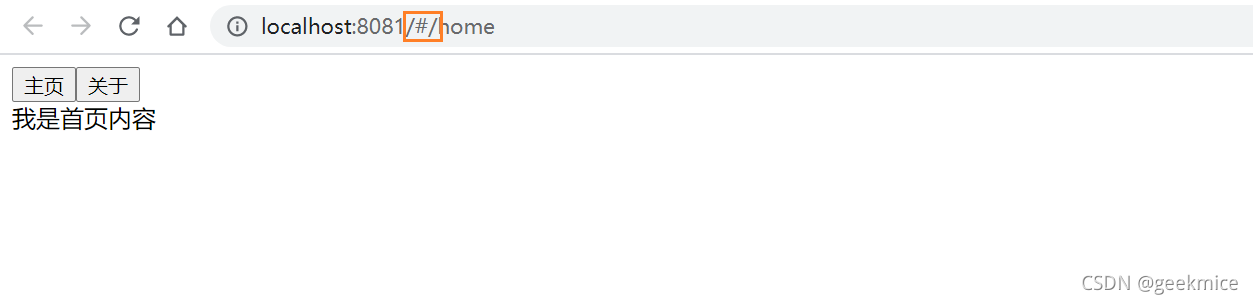
想要改成html5中history,可以进行一下配置
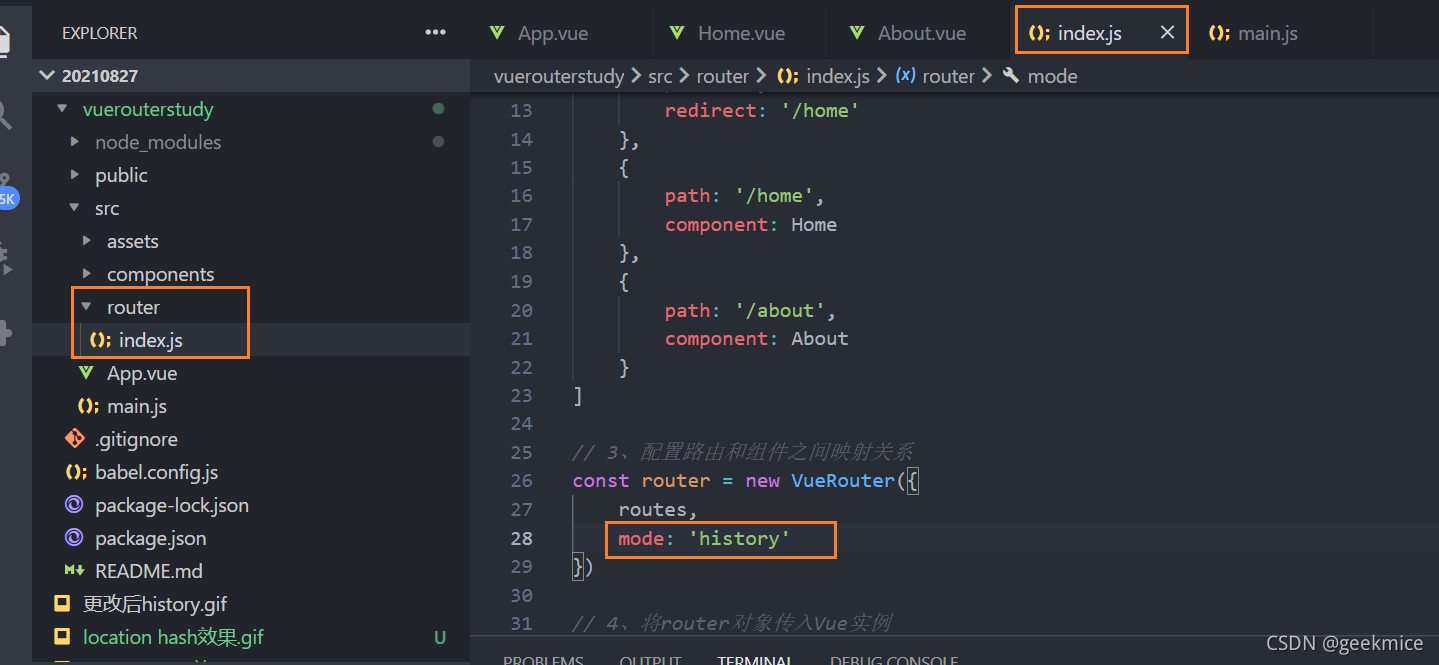
修改后
3.5、router-link补充
- tag属性:tag可以指定之后渲染成什么组件, 比如上面的代码会被渲染成一个元素, 而不是
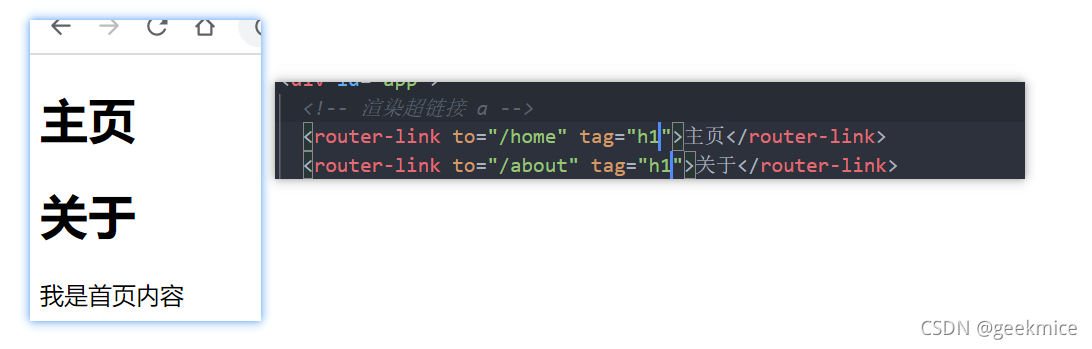
- replace属性:replace不会留下history记录, 所以指定replace的情况下, 后退键返回不能返回到上一个页面中
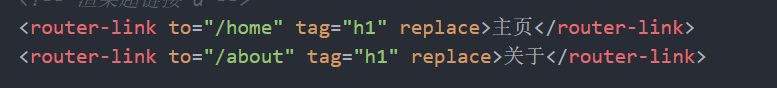
- active-class属性: 当对应的路由匹配成功时, 会自动给当前元素设置一个router-link-active的class, 设置active-class可以修改默认的名称.
在进行高亮显示的导航菜单或者底部tabbar时, 会使用到该类.
但是通常不会修改类的属性, 会直接使用默认的router-link-active即可.
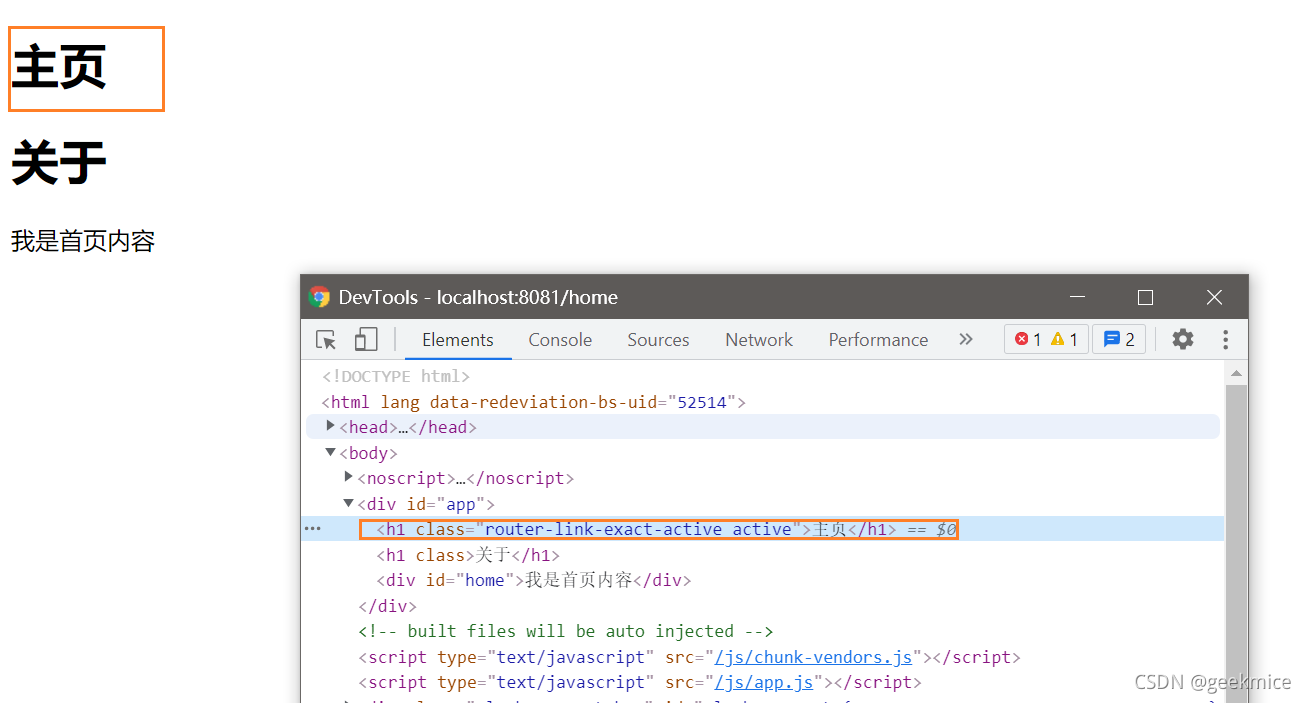
也可以通过这种方式 在路由配置的index.js
3.6、路由代码跳转
源码实现
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 渲染超链接 a -->
<!-- <router-link to="/home" tag="h1" replace>主页</router-link> -->
<!-- <router-link to="/about" tag="h1" replace active-class>关于</router-link> -->
<button @click="handleHome">主页</button>
<button @click="handleAbout">关于</button>
<!-- 动态渲染组件 -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: {},
methods:{
handleHome(){
this.$router.push('/home')
},
handleAbout(){
this.$router.push('/about')
}
}
};
</script>
<style></style>
效果图

3.7、动态路由
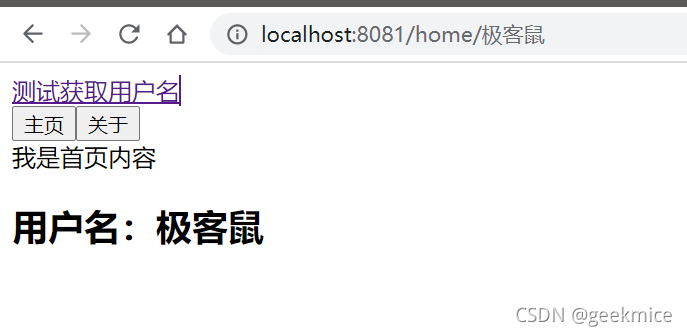
在某些情况下,一个页面的path路径可能是不确定的,比如我们进入用户界面时,希望是如下的路径:
/user/aaaa或/user/bbbb
除了有前面的/user之外,后面还跟上了用户的ID
这种path和Component的匹配关系,我们称之为动态路由(也是路由传递数据的一种方式)。
1、配置组件和路径的映射关系
// 配置路由相关的信息
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
import Home from '../components/Home'
import About from '../components/About'
import User from '../components/User'
// 通过Vue.use(插件),安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
},
<!--这是关键代码-->
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: User
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode: "history",
linkActiveClass: "active"
})
// 将router对象传入Vue实例
export default router
2、创建组件User User.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>我是APP页面</h1>
{{$route.params.id}}
</div>
</template>
3、首页显示
App.vue
<router-link to="/home/极客鼠" >测试获取用户名</router-link><br>
4、效果图
4、路由的懒加载
4.1、认识懒加载
官方给出了解释:
当打包构建应用时,Javascript 包会变得非常大,影响页面加载。
如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就更加高效了
官方在说什么呢?
首先, 我们知道路由中通常会定义很多不同的页面.
这个页面最后被打包在哪里呢? 一般情况下, 是放在一个js文件中.
但是, 页面这么多放在一个js文件中, 必然会造成这个页面非常的大.
如果我们一次性从服务器请求下来这个页面, 可能需要花费一定的时间, 甚至用户的电脑上还出现了短暂空白的情况.
如何避免这种情况呢? 使用路由懒加载就可以了.
路由懒加载做了什么?
路由懒加载的主要作用就是将路由对应的组件打包成一个个的js代码块.
只有在这个路由被访问到的时候, 才加载对应的组件
4.2、懒加载效果
// 配置路由相关的信息
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
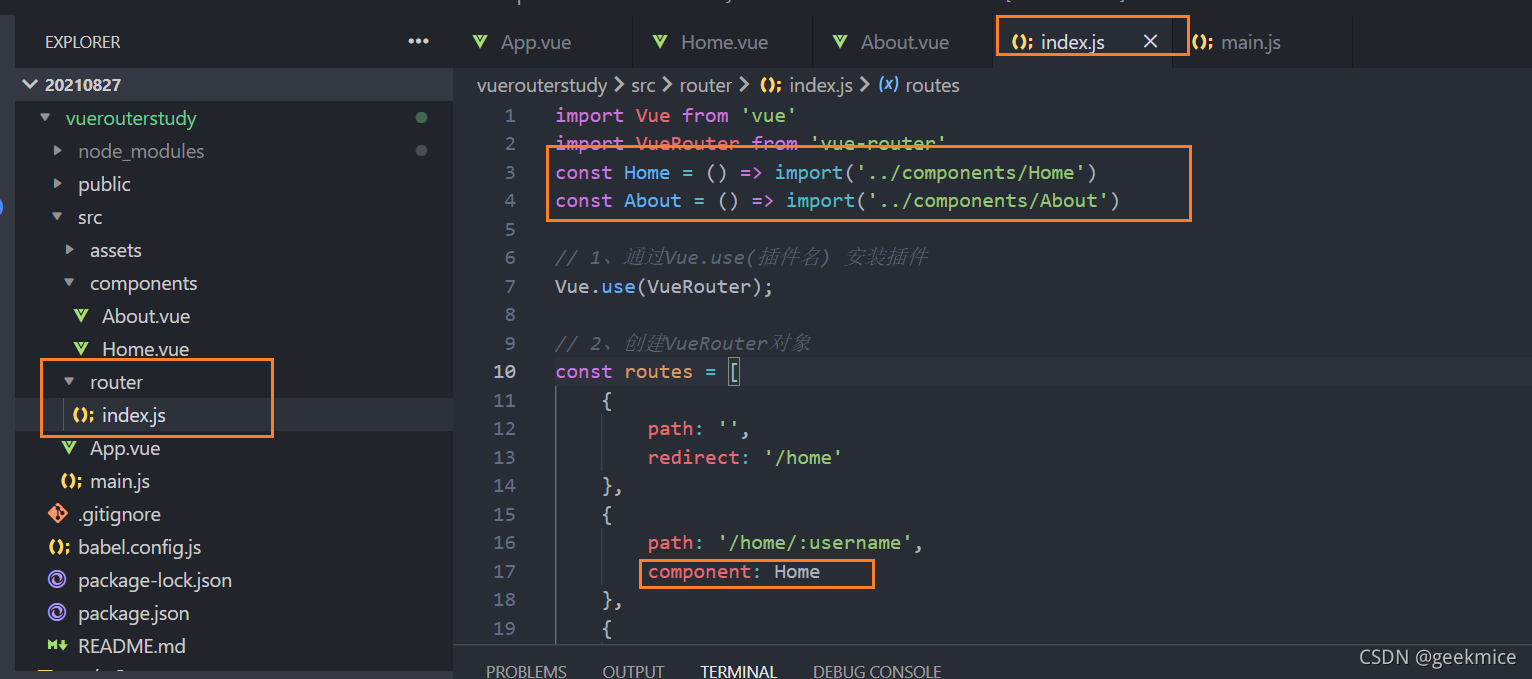
const Home = () => import ('../components/Home')
const About = () => import ('../components/About')
const User = () => import ('../components/User')
// 通过Vue.use(插件),安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
}, {
path: '/user/:id',
component: User
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode: "history",
linkActiveClass: "active"
})
// 将router对象传入Vue实例
export default router
4.3、懒加载方式
5、路由的嵌套使用
5.1、认识嵌套路由
嵌套路由是一个很常见的功能
比如在home页面中, 我们希望通过/home/news和/home/message访问一些内容.
一个路径映射一个组件, 访问这两个路径也会分别渲染两个组件.
组件和路径关系

5.2、实现过程
1、创建两个组件Message,News
Message.vue
<template> <div id="about">最新消息</div> </template> <script> </script>
News.vue
<template> <div id="about">新闻内容</div> </template> <script> </script>
2、配置路由信息 主要是子路由
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
const Home = () => import('../components/Home')
const About = () => import('../components/About')
const Message = () => import('../components/Message')
const News = () => import('../components/News')
// 1、通过Vue.use(插件名) 安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter);
// 2、创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path:'/home',
component:Home,
children:[
{
path:'news',
component: News
},
{
path:'message',
component: Message
}
]
},
{
path: '/home/:username',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
}
]
// 3、配置路由和组件之间映射关系
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode: 'history',
// linkActiveClass: 'active'
})
// 4、将router对象传入Vue实例
export default router

3、父组件渲染子组件信息
Home.vue
<template>
<div id="home">
我是首页内容<br>
<router-link to="/home/news"> 新闻</router-link>
<router-link to="/home/message"> 消息</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
<!-- <h2>用户名:{{ $route.params.username }}</h2> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
};
</script>
4、效果图
5.3、嵌套路由的默认路径
重定向redirect
{
path: '/user',
component: User,
children: [
{
path: 'message',
component: Message,
},
{
path: 'news',
component: News,
},
// 重定向 /user/news
{
path: '',
redirect: 'news',
},
]
},
6、路由传递参数
传递参数主要有两种类型:params和query
params类型
1.配置路由格式:/router/:id
2.传递的方式:在path后面跟上对应的值
3.传递后形成的路径:/router/123,/router/abc
query类型
1.配置路由格式:/router,也就是普通配置
2.传递方式:对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
3.传递后形成的路径:/router?id=123,/router?id=abc
6.1、准备工作
传递参数之一:router-link
1、创建组件Profile.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是Profile页面</h2>
<p>我是profile页面具体内容</p>
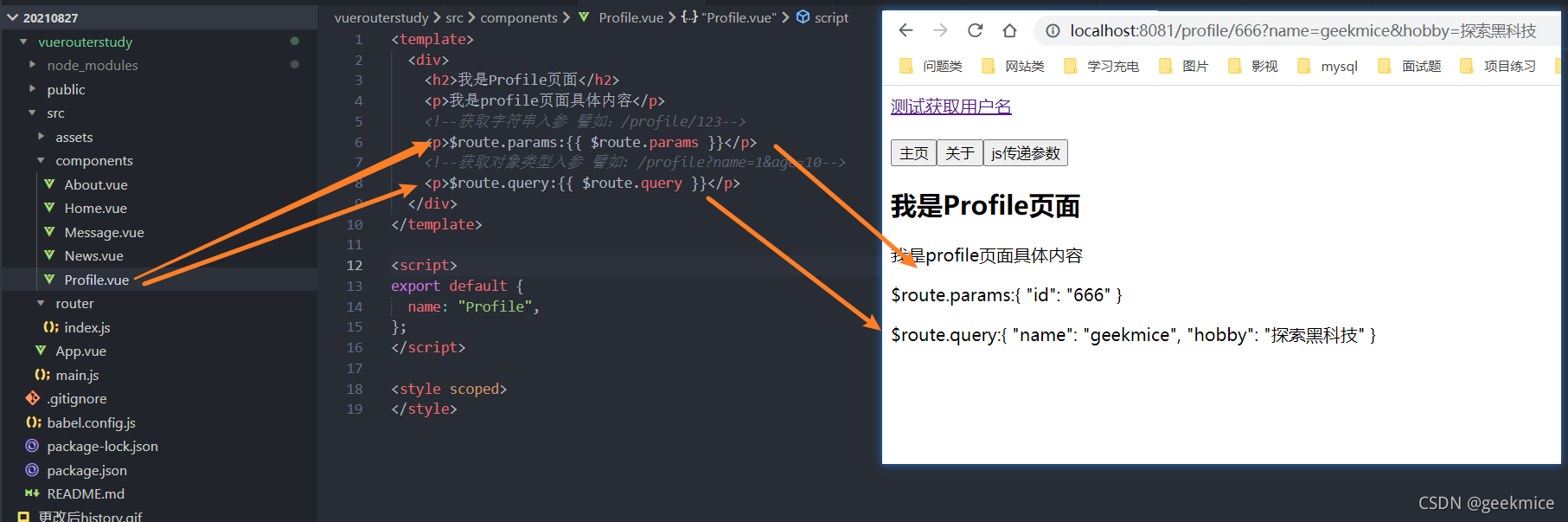
<!--获取字符串入参 譬如:/profile/123-->
<p>$route.params:{{ $route.params }}</p>
<!--获取对象类型入参 譬如: /profile?name=1&age=10-->
<p>$route.query:{{ $route.query }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Profile",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2、配置路由
const Profile = () => import('../components/Profile')
{
path: '/profile/:id',
component: Profile
}
3、app.vue 页面显示
<router-link
:to="{
path: '/profile/' + 123,
query: { name: 'geekmice', hobby: '篮球' }
}"
tag="button"
>router-link传递参数</router-link
>
4、最终效果

传递参数之二:js实现
<button @click="jsTransferParams">js传递参数</button>
jsTransferParams() {
this.$router.push({
path: "/profile/" + 666,
query: { name: "geekmice", hobby: "探索黑科技" },
});
},
profile.vue获取参数
<p>$route.params:{{ $route.params }}</p>
<p>$route.query:{{ $route.query }}</p>

6.2、获取参数
获取参数通过$route对象获取的.
在使用了vue-router应用中,路由对象会被注入每个组件中,赋值为this.$route,并且路由切换时候,路由对象会被更新。
$route传递的信息如下
6.3、router和route区别
简单理解 即一个获取路由信息,一个是用来操作路由的;
$router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法
路由的跳转方法,钩子函数等
$route为当前router跳转对象里面可以获取name、meta、path、hash、query、params、fullPath、matched、redirectedFrom等
7、路由导航守卫
vue-router提供的导航守卫主要用来监听路由的进入和离开的
vue-router提供了beforeEach和afterEach的钩子函数,它们会在路由即将改变前和改变后触发
利用beforeEach完成标题的修改
- 首先,我们可以在钩子中定义一些标题,可以利用meta来定义
- 其次,利用导航守卫,修改我们的标题
// 配置路由相关的信息
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from "vue-router"
const Home = () => import('../components/Home')
const About = () => import('../components/About')
const User = () => import('../components/User')
const Message = () => import('../components/Message')
const News = () => import('../components/News')
const Profile = () => import('../components/Profile')
// 通过Vue.use(插件),安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
meta: {
title: "首页"
}
},
{
path: '/profile/:id',
component: Profile,
meta: {
title: "档案"
}
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
meta: {
title: "关于"
}
}, {
path: '/user',
component: User,
children: [
{
path: 'message',
component: Message,
},
{
path: 'news',
component: News,
},
{
path: '',
redirect: 'news',
},
]
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode: "history",
linkActiveClass: "active"
})
router.afterEach((to, from, next) => {
document.title = to.matched[0].meta.title;
next()
})
// 将router对象传入Vue实例
export default router
效果图
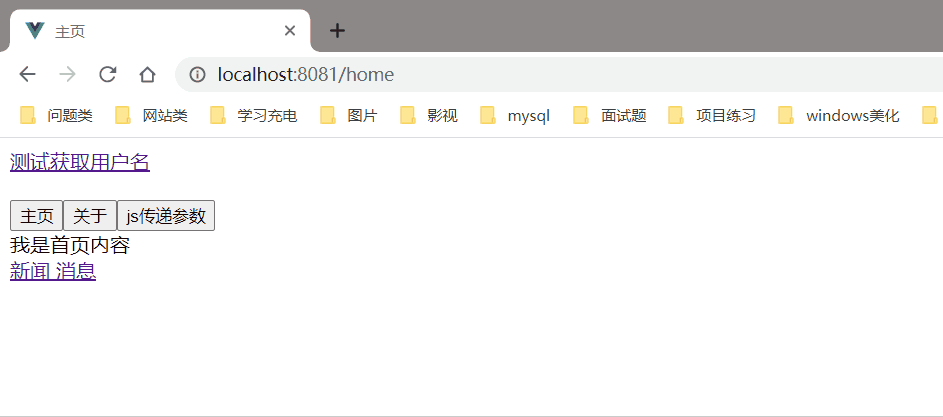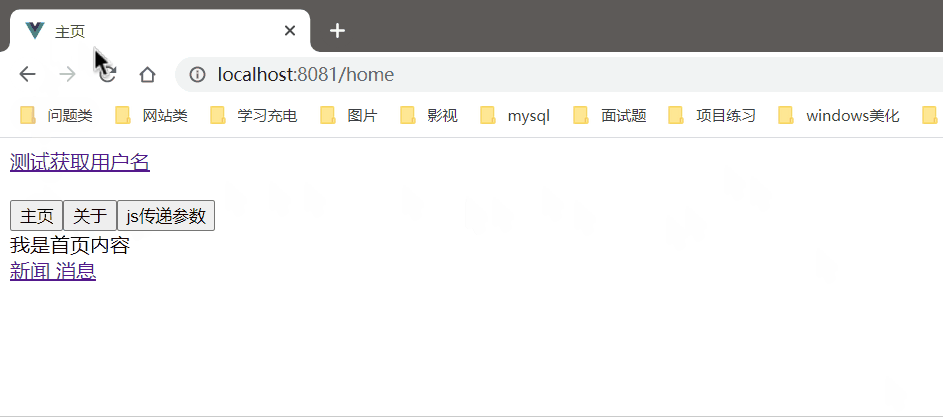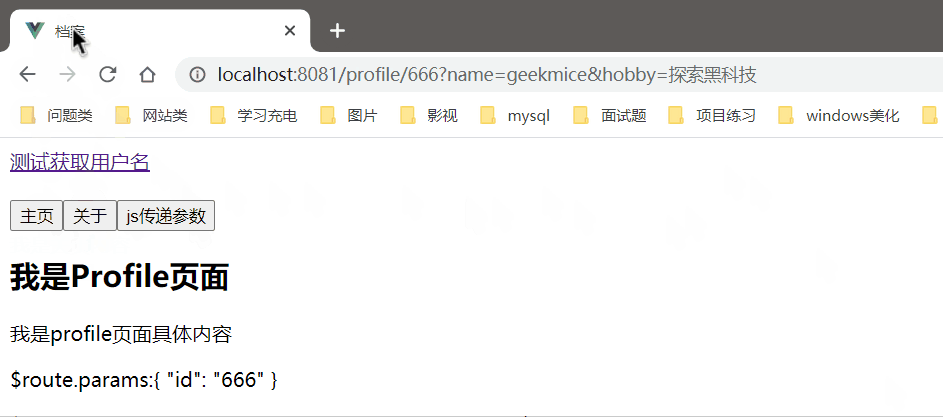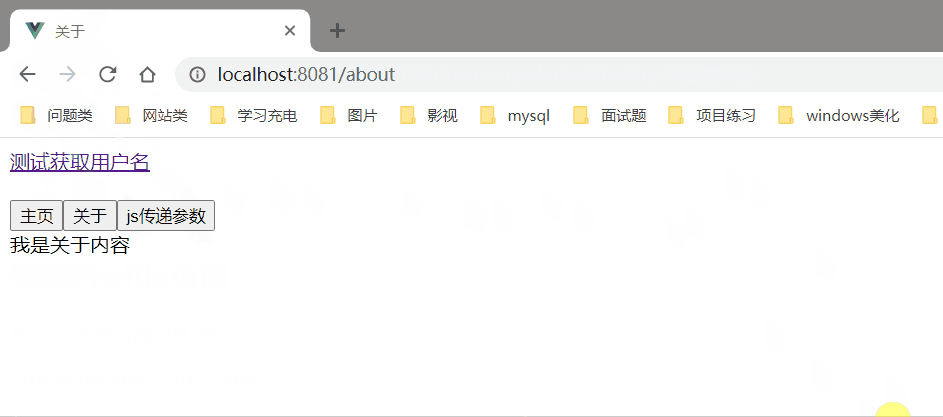
简要说明
导航钩子的三个参数解析
- to: 即将要进入的目标的路由对象
- from: 当前导航即将离开的路由对象
- next调用该方法之后,才能进入下一个钩子
8、keep-alive
这个组件 Vue的内置组件,能在组件切换过程中将状态保留在内存中,防止重复渲染DOM。
案例说明理解一下
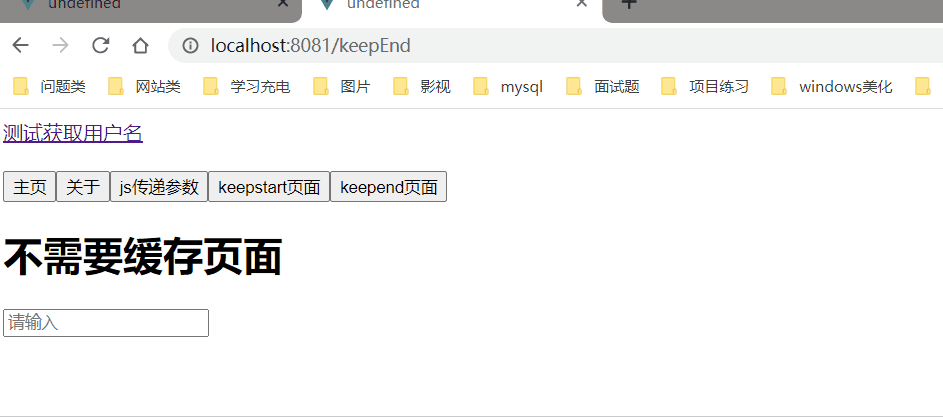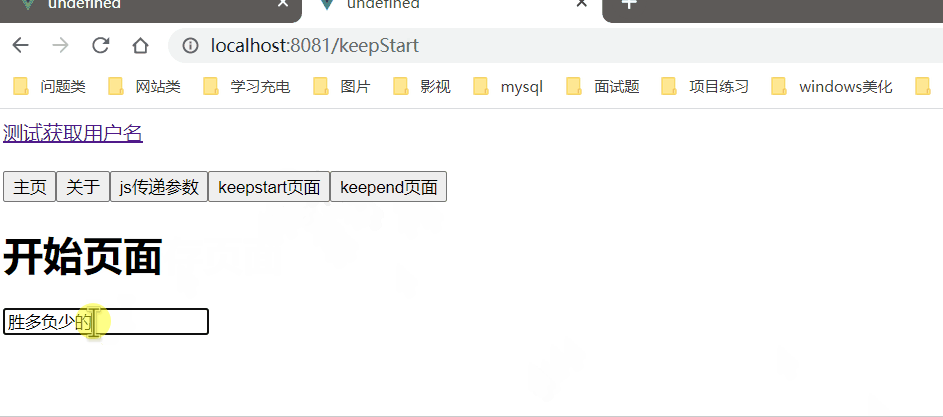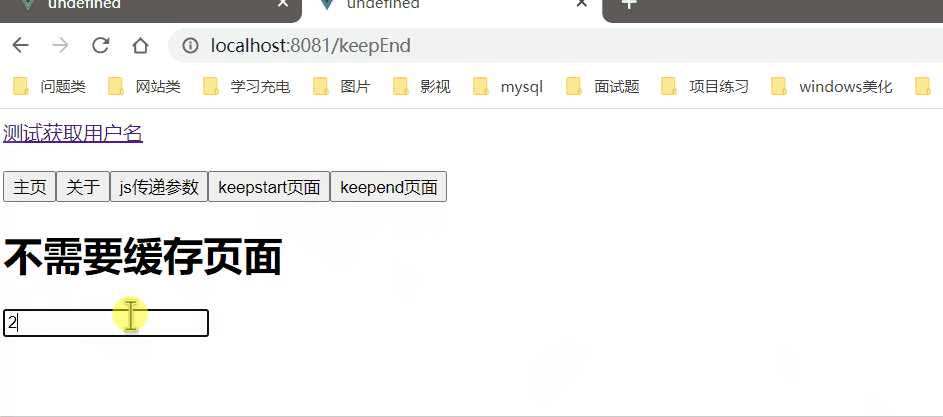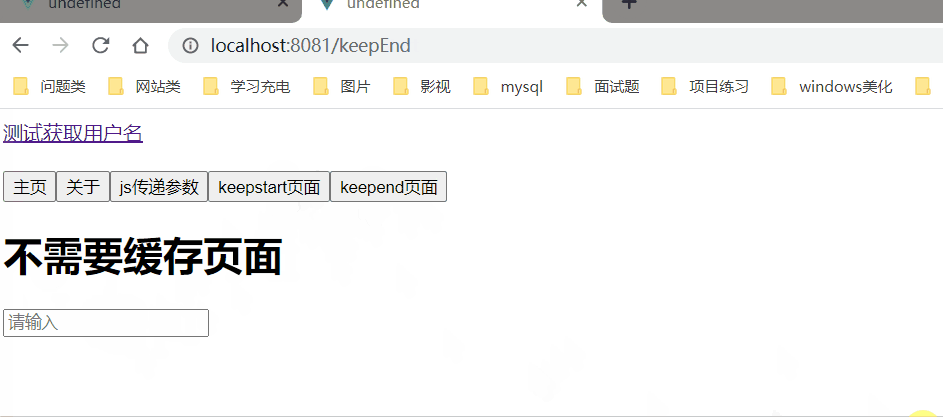
需求:现在有两个组件KeepStart,KeepEnd组件,KeepStart组件 有input输入框,输入信息 可以缓存 KeepEnd组件不能缓存
源码实现
1、KeepStart.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>开始页面</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入。。。">
</div>
</template>
2、KeepEnd.vue
<template>
<div>
<h1>不需要缓存页面</h1>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入">
</div>
</template>
3、router->index.js
const KeepStart = () => import('../components/KeepStart')
const KeepEnd = () => import('../components/KeepEnd')
{
path: '/keepStart',
component: KeepStart,
name:'keepStart',
meta: {
keepAlive: true
}
},
{
path: '/keepEnd',
name:'keepEnd',
component: KeepEnd,
meta: {
keepAlive: false
}
}
4、App.vue
<router-link to="/keepStart" tag="button">keepstart页面</router-link>
<router-link to="/keepEnd" tag="button">keepend页面</router-link>
<!-- 动态渲染组件 -->
<!-- <router-view></router-view> -->
<keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="$route.meta.keepAlive"></router-view>
</keep-alive>
<router-view v-if="!$route.meta.keepAlive"></router-view>
效果图
9、TabBar练习
9.1、需求表述
效果图

表述
实现一个导航栏,分别是分类,首页,购物车,我的四个栏目;用户点击各自的栏目显示不同页面;采用插槽的思想来实现可扩展性。
9.2、需求分析
- 1、如果在下方有一个单独的TabBar组件,如何安装
自定义TabBar组件,在APP中使用
让Tabbar处于底部,设置相关的样式
- 2、TabBar中显示的内容由外部决定
定义插槽
flex布局评分TabBar
- 3、自定义TabBarItem,可以传入图片和文字
定义TabBarItem,并且定义两个插槽:图片,文字
给两个插槽外层包装div,用于设置样式
填充插槽,实现底部TabBar的效果
- 4、传入选中高亮图片
定义另外一个插槽,插入active-icon的数据
定义个变量isActive,通过v-show来决定是否显示对应的icon
- 5、TabBarItem绑定路由数据
安装路由 npm install vue-router –save
完成router->index.js,创建对应的组件
main.js注册router
App.vue加入router-view组件 渲染
- 6、点击item跳转到对应路由表,并且动态绝对isActive
监听item的点击,通过this.$router.replace()替换路由路径
通过this.$route.path.indexOf(this.link) !== -1 来判断是否是active
- 7、动态计算active样式
封装新的计算属性 this.isActive ? {‘color’:‘red’}:{}
9.3、需求实现
实现版本1
创建vue项目
vue create navbar
删除无用的组件 HelloWorld 图片
简易目录结构
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="tab-bar">
<div id="tab-bar-item">首页</div>
<div id="tab-bar-item">分类</div>
<div id="tab-bar-item">购物车</div>
<div id="tab-bar-item">我的</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: {},
};
</script>
<style>
/* 引入css样式 */
@import url("./assets/css/base.css");
#tab-bar {
display: flex;
background-color: rgb(246, 246, 246);
/* 绝对定位 */
position: fixed;
left: 0;
bottom: 0;
right: 0;
}
#tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
}
</style>
base.css
body{
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
效果图

最终版本
目录结构
关键源码实现
TabBar.vue 封装
<template>
<div id="tab-bar">
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBar"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
#tab-bar {
display: flex;
background-color: #f6f6f6;
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
box-shadow: 0 -1px 1px rgba(100,100,100,.2);
}
</style>
TabBarItem.vue 封装
<template>
<!--所有的item都展示同一个图片, 同一个文字-->
<div class="tab-bar-item" @click="itemClick">
<div v-if="!isActive"><slot name="item-icon"></slot></div>
<div v-else><slot name="item-icon-active"></slot></div>
<div :style="activeStyle"><slot name="item-text"></slot></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
props: {
path: String,
activeColor: {
type: String,
default: 'red'
}
},
data() {
return {
// isActive: true
}
},
computed: {
isActive() {
// /home -> item1(/home) = true
// /home -> item1(/category) = false
// /home -> item1(/cart) = true
// /home -> item1(/profile) = true
return this.$route.path.indexOf(this.path) !== -1
},
activeStyle() {
return this.isActive ? {color: this.activeColor} : {}
}
},
methods: {
itemClick() {
this.$router.replace(this.path)
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.tab-bar-item img {
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
margin-top: 3px;
vertical-align: middle;
margin-bottom: 2px;
}
</style>
配置路由 index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
const Home = () => import('../views/home/Home')
const Category = () => import('../views/category/Category')
const Cart = () => import('../views/cart/Cart')
const Profile = () => import('../views/profile/Profile')
// 1.安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2.创建路由对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/category',
component: Category
},
{
path: '/cart',
component: Cart
},
{
path: '/profile',
component: Profile
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode: 'history'
})
// 3.导出router
export default router
最终效果

到此这篇关于详解VueRouter 路由的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关VueRouter 路由内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!