目录
- 介绍
- routes中对象属性
- path: string
- component : Component | () => import(组件)
- name: string
- redirect: string | Location | Function
- props: boolean | Object | Function
- alias: string| Array[string]
- children?: Array[RouteConfig]
- beforeEnter: (to: Route, from: Route, next: Function) => void
- Router的实例方法
- *VueRouter实例属性
- VueRouter实例方法
- router.push(string | location)
- router.replace(string | location)
- router.go(Int number)
- router.back()
- router.forward()
- 路由懒加载
- 没有使用懒加载
- 使用懒加载
- history模式和hash模式
- history模式
- hash模式
- 路由守卫
- 全局路由守卫
- 情况一
- 情况二
- 情况三
介绍
在使用vue-router的项目中,实例化VueRouter是其配置选项routes该选项指定路由与视图的组件的关系或者路由与其他路由的关系,Router配置选项中是其中最重要的配置。
routes中对象属性
interface RouteConfig = {
path: string,
component?: Component,
name?: string, // 命名路由
*components?: { [name: string]: Component }, // 命名视图组件 https://router.vuejs.org/zh/guide/essentials/named-views.html#%E5%B5%8C%E5%A5%97%E5%91%BD%E5%90%8D%E8%A7%86%E5%9B%BE
redirect?: string | Location | Function,
props?: boolean | Object | Function,
alias?: string | Array<string>,
children?: Array<RouteConfig>, // 嵌套路由
beforeEnter?: (to: Route, from: Route, next: Function) => void,
*meta?: any,
// 2.6.0+
*caseSensitive?: boolean, // 匹配规则是否大小写敏感?(默认值:false)
*pathToRegexpOptions?: Object // 编译正则的选项
}
path: string
指定当前路由的路径,当浏览器url与path匹配时router-view就会渲染当前route对象指定视图组件component/components
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
component: Home
},
{
path:'/user',
component: User
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
注意Vue的router支持动态路径,以 “/:属性名”形式作为当前path字符串中的一部分。这段字符串路由将作为动态路由匹配真实url上响应字符串信息
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
component: Home
},
{
path:'/user/:id/:local', // 动态路径 :id :local
component: User
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
})
// 路由跳转
<div id="app">
<router-view />
// 下面这些链接都会与/user/:id/:local匹配
<router-link to="/user/007/lk">用户007</router-link>
<router-link to="/user/111/js">用户111</router-link>
<router-link to="/user/10086/yk">用户10086</router-link>
<router-link to="/user/241247/la">用户241247</router-link>
</div>
/* 当我们跳转至上面的路由时其对应的路由视图组件User内部就可以通过
this.$route.params 获取到动态路径匹配到的信息
例子: url /user/007/lk this.$route.params -> {id:'007',local:'lk'}
url /user/10086/yk this.$route.params -> {id:'10086',local:'yk'}
*/
注意this.$route就是当前vue应用程序所在路由的信息对象
// http://localhost:8080/#/user/10086/cc?wd=iPhone&aa=test
{
name: undefined, // 当前路由名
*fullPath: "/user/10086/cc" // 当前url完整路径
*hash: "" // 当前路由的哈希
*matched: [{…}]
*meta: {}
params: {id: "10086", local: "cc"} // 动态路径匹配到键值对对象
*path: "/user/10086/cc" // 当前url匹配到的路径
query: { // url的query字符串网址?后面的参数解析出来的对象
wd: "iPhone",
aa: "test"
}
}
component : Component | () => import(组件)
当前浏览器url与路由的path匹配时所渲染的路由组件
import Vue from 'vue'
import HotMusicList from '../views/HotMusicList'
const routes = [
{
path: '/hot',
component: HotMusicList
},
{
// 动态路径匹配 通过:id获取每一首歌不同的id
path: '/music/:id',
// 路由的懒加载,通过函数的形式,可以让项目中哪些不许一开始就要加载的组件,加载到项目中去
// 只有浏览器跳转到当前路由时,该路由组件才会加载到项目中去
// 这样做的好处是减少不必要的加载降低应用加载速度和运行带宽
component: () => import('../views/MusicPlay')
}
]
注意在项目开发中应用中不需要一开始就加载的路由组件请使用懒加载
name: string
给路由命名,让路由成为具名路由。路由的导航就可以使用name进行跳转。(路由使用location导航时只有具名路由可可以直接接受pramas传参)
const routes = [
{
path: '/user',
name: 'User',
component: () => import('../views/User.vue')
}
]
redirect: string | Location | Function
重定向路由,当前应用访问导航至该路由时,这个路由会(以替换的形式)自动重定向到redirect指定的新路由
const routes = [
{
path: '/contact',
component: ContactView
},
{
path: '/user/:id',
name: 'User',
component: () => import('../views/User.vue')
},
{
path: '/oldpath1',
redirect: '/contact'
},
{
path: '/oldpath2',
redirect: { name: 'User', params: { name: '小明', age: 19 } }
},
/*
redirect 支持函数的形式,该函数接收一个参数就是个访问oldpath时生成的location对象
redirect 函数的形式必须返回重定向路由的path或location
*/
{
path: '/oldpath2',
redirect:(oldpathLocation) => '/contact'
}
{
path: '/oldpath4',
redirect:(oldpathLocation) => { name: 'User', params: { name: '小明', age: 19 } }
}
]
props: boolean | Object | Function
路由的动态匹配一般情况下只能通过,this.$route.params获取动态匹配到的值。当设置props属性后动态匹配到的键值对可以作为组件props直接传递给视图组件,这样大大降低组件的耦合性
布尔值.如果 props 被设置为 true,route.params 所有键值对将会被设置为组件props属性。
const routes = [
{
path: '/hot',
component: HotMusicList
},
{
// 动态路径匹配 通过:id获取每一首歌不同的id
path: '/music/:id',
// 路由的懒加载
component: () => import('../views/MusicPlay'),
props: true
}
]
// 组件内部 就可通过props的id 访问到this.$route.id
<template>
<div>
歌曲播放
<audio controls :src="musicUrl"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props: ['id'], // 路由动态路径匹配到的键值对会自动传递给当前组件的同名props
data() {
return {
musicUrl: ''
}
},
created() {
fetch(`/song/url?id=${this.id}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then(({ data }) => {
//真实开发中这里要判断数据是否请求成功
console.log(data[0]);
// 把歌曲的数据赋值给data
this.musicUrl = data[0]?.url
});
},
};
</script>
对象props对象形式,就是将对象key作为渲染组件props属性名,value就是对应属性值 (这种写法value不会改变所以传递props都是一些静态属性)
{
path: '/home/:id',
name: 'Home',
props: {
a: 1,
b: false
},
component: Home
}
函数props的函数写法接收当前路由信息对象作为参数,该函数会返回一个对象.对象的key就是渲染组件props属性名,value就是对应属性值
{
path: '/home/:id',
name: 'Home',
props: (route) => ({
a: route.query.wd, //将路由query.wd传递给组件Home的a props
b: route.params.id //将路由params.id传递给组件Home的b props
}),
component: Home
}
alias: string| Array[string]
路由的别名,可以给一个路由设置多个路径。当访问这些别名路径时都会访问同一个路由组件
const routes = [
{
path: '/hot',
component: HotMusicList,
alias: ['/list','/rank','recommend']
}
]
children?: Array[RouteConfig]
嵌套路由,可以给当前路由设置二级路由
[
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
children: [
{
path: '/home/follow',
component: () => import('../views/home/Follow')
},
{
path: 'recommend', //路由前不加/相对路径等价于 "/home/recommed"
component: () => import('../views/home/Recommend')
}
]
}
]
beforeEnter: (to: Route, from: Route, next: Function) => void
路由的独享守卫,当应用将要导航到当前路由时,可以使用该守卫进行一些逻辑运算实现是否阻止本次导航
Router的实例方法
概念将VueRouter实例对象配置到Vue中后, vue实例就会拥有一个this.$router属性,this.$router就是当前VueRouter的实例对象。他提供了所有编程式导航的API。
注意router是路由实例对象里面包含着路由的属性方法,router是路由实例对象里面包含着路由的属性方法, router是路由实例对象里面包含着路由的属性方法,route是当前浏览访问url路由信心对象
*VueRouter实例属性
- app 配置了 当前router 的 Vue 根实例
- mode 当前Router使用的模式 “hash” | “history”
- currentRoute 当前路由对应的route信息对象
VueRouter实例方法
router.push(string | location)
编程式导航到指定的路由
<template>
<div>
<h3>主页</h3>
<div class="tab">
<router-link to="/home/follow">关注</router-link>|
<button @click="gotoRecommend">推荐</button>
</div>
<router-view />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
gotoRecommend() {
// this.$router.push("/home/recommend");
this.$router.push({path:"/home/recommend", query:{wd:1,offset:0}})
},
},
};
</script>
router.replace(string | location)
编程式替换当前路由导航到新路由
<template>
<div>
<h3>主页</h3>
<div class="tab">
<router-link to="/home/follow">关注</router-link>|
<button @click="gotoRecommend">推荐</button>
</div>
<router-view />
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
gotoRecommend() {
// this.$router.replace("/home/recommend");
this.$router.replace({path:"/home/recommend", query:{wd:1,offset:0}})
},
},
};
</script>
router.go(Int number)
编程式从当前路由history栈的位置前进后退number条
this.$router.go(3) // 从当前路由history栈的位置前进3条 this.$router.go(-1) // 从当前路由history栈的位置后退1条 this.$router.go(0) // 强制刷新页面
注意当前进/后退的number大于实例路由history栈的长度时,会前进到最后一条或后退到第一条,但是不推荐这样做会引起性能问题造成页面卡顿
router.back()
编程式从当前路由history栈的位置后退1条
this.$router.back() // 等价于this.$router.go(-1)
router.forward()
编程式从当前路由history栈的位置前进1条
this.$router.forward() // 等价于this.$router.go(1)
路由懒加载
用vue.js写单页面应用时,会出现打包后的JavaScript包非常大,影响页面加载,我们可以利用路由的懒加载去优化这个问题,当我们用到某个路由后,才去加载对应的组件,这样就会更加高效
没有使用懒加载
先引入了组件,事先加载好了。然后不管有没有使用都已经存在
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
使用懒加载
只有路由被使用到了才进行加载对应的组件
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/mock',
name: 'Mock',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/Mock.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
history模式和hash模式
vue-router 默认 hash 模式 —— 使用 URL 的 hash 来模拟一个完整的 URL,于是当 URL 改变时,页面不会重新加载。
如果不想要很丑的 hash,我们可以用路由的 history 模式,这种模式充分利用 history.pushState API 来完成 URL 跳转而无须重新加载页面。
history模式
history —— 利用了 HTML5 History Interface 中新增的 pushState() 和 replaceState() 方法。(需要特定浏览器支持)这两个方法应用于浏览器的历史记录栈,在当前已有的 back、forward、go 的基础之上(方法可在Router的实例方法中查看),它们提供了对历史记录进行修改的功能。只是当它们执行修改时,虽然改变了当前的 URL,但浏览器不会立即向后端发送请求。
手动设置
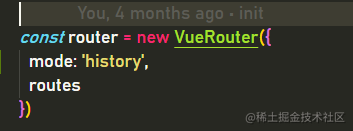
效果
![]()
hash模式
hash —— 即地址栏 URL 中的 # 符号(此 hash 不是密码学里的散列运算)。比如这个 URL:http://localhost:8081/#/form hash 的值为 #/form。它的特点在于:hash 虽然出现在 URL 中,但不会被包括在 HTTP 请求中,对后端完全没有影响,因此改变 hash 不会重新加载页面。
![]()
路由守卫
全局路由守卫
- router.beforeEach 前置守卫
- *router.beforeResolve 前置守卫
- *router.afterEach 后置守卫
情况一
在使用vue-router开发的项目中,一般情况下不同路由之间的切换会将离开的路由组件卸载,进入的路由组件挂载。
这种情况下我们可通过vue的声明周期进行一些页面的逻辑操作。但是如果有些情况下应用为提高用户体验减少卸载频率或者保存离开组件的活跃性,使用keep-alive组件包裹router-view后路由的切换就把会卸载离开的组件了。这时,如果你的组件需要在路由进入或离开时进行一些操作修改组件自身的数据DOM编程等,就不能再依靠vue的生命周期了。这种情况下请使用组件内的路由守卫。
- beforeRouteEnter 路由组件将要进入
- beforeRouteUpdate (2.2 新增) 路由组件将要更新 -> /music/10086 /music/10010
- beforeRouteLeave 路由组件将要离开
export default {
props: ['id'],
data() {
return {
musicUrl: ''
}
},
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
// 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用
// 不!能!获取组件实例 `this`
// 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建
console.log(undefined)
},
beforeRouteUpdate (to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候,
// 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
},
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
}
}
注意组件独享的路由守卫方法都包含三个参数 to from next
- to : location 本次路由导航跳转的目标路由信息对象
- from : location 本次路由导航从哪个路由信息对象跳转而来()
- next : function 该方法是否允许本次路由跳转
next() // 允许路由跳转
next(true) // 允许路由跳转
next(false) // 不允许路由跳转
next('/') / next({ path: '/' }) // 跳转到一个不同的地址。当前的导航被中断,然后进行一个新的导航。你可以向 next 传递任意位置对象,且允许设置诸如 replace: true、name: 'home' 之类的选项。
// 注意 只有beforeRouteEnter 的next方法可以接受一个回调函数,
// 该回调函数接收当前路由组件实例对象作为参数,我们可以通过该参数操作当前组件
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
console.log(to , from)
console.log('组件将要进入,这是组件实例还不存在',this)
next(vm => {
fetch(`/song/url?id=${vm.id}`)
.then((res) => res.json())
.then(({ data }) => {
//真实开发中这里要判断数据是否请求成功
console.log(data[0]);
// 把歌曲的数据赋值给data
vm.musicUrl = data[0]?.url
});
}) // 允许路由跳转
}
情况二
在使用vue-router开发的项目中,一般情况下不同路由之间的切换会将离开的路由组件卸载,进入的路由组件挂载。
这种情况下我们可通过vue的声明周期进行一些页面的逻辑操作。但是如果有些情况下应用为提高用户体验减少卸载频率或者保存离开组件的活跃性,使用keep-alive组件包裹router-view后路由的切换就吧会卸载离开的组件了这时,如果你的组件需要在路由进入或离开时进行一些操作不需要修改组件自身的状态只是判断是否允许本次路由的跳转等。这种情况下请使用路由独享守卫。
beforeEnter(to, from, next) 当路由将要导航至当前路由时触发
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo,
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
// ...
}
}
]
})
案例 登录验证 路由独享守卫配置
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/discover',
component: () => import('../views/Discover')
},
{
path: '/mine',
component: () => import('../views/Mine'),
//路由独享守卫
beforeEnter(to, from, next) {
// 因为这个守卫没有任何DOM操作或者对组件自身状态进行读写
// 这样的守卫就可以作为路由独享守卫
// 正确的做法存在cookie storage中
if (localStorage.getItem("user")) {
next();
} else {
// 这里吗没有this, next接收一个回调函数,在回调函数中跳转
// 下面的写法进入了个人页面,又从个人页面重定向到登录,这样可能会造成一些不必要的bug
// next((vm) => {
// vm.$router.replace('/landr')
// });
next({name:'login',params:{to}}); //阻止本次跳转,直接导航到指定路由
}
}
},
{
path: '/landr', // login an register
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/LoginAndRegister'),
children: [
{
name:'login',
path: 'login',
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/Login')
},
{
path: 'register',
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/Register')
}
]
}
]
情况三
全局路由守卫,当应用中有多个路由都需要进行相同逻辑的路由守卫判断时,并且该逻辑操作中不需要直接操作组件DOM或组件组件的状态这是就可以使用全局路由守卫(全局守卫最常见的应用就是登陆验证)
beforeEach(to,from,next) 全局前置守卫
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home'
Vue.use(Router)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/discover',
name: 'Discover',
component: () => import('../views/Discover')
},
{
path: '/mine',
name: 'Mine',
component: () => import('../views/Mine'),
},
{
path: '/landr', // login an register
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/LoginAndRegister'),
children: [
{
name: 'login',
path: 'login',
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/Login')
},
{
path: 'register',
component: () => import('../views/loginanregister/Register')
}
]
}
]
const router = new Router({
routes,
linkExactActiveClass: 'active'
})
// 路由的全局守卫所有的路由跳转,都会调用该守卫
// 全局路由守卫也是Vue router应用中,最适合做登录验证的地方
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if(to.name === "Mine" || to.name === "Discover") {
// 因为这个守卫没有任何DOM操作或者对组件自身状态进行读写
// 这样的守卫就可以作为路由独享守卫
// 正确的做法存在cookie storage中
if (localStorage.getItem("user")) {
next();
} else {
// 这里吗没有this, next接收一个回调函数,在回调函数中跳转
// 下面的写法进入了个人页面,又从个人页面重定向到登录,这样可能会造成一些不必要的bug
// next((vm) => {
// vm.$router.replace('/landr')
// });
next({ name: 'login', params: { to } }); //阻止本次跳转,直接导航到指定路由
}
}else {
next()
}
})
export default router
router.beforeResolve(to,from,next) 全局前置守卫,在beforeEach触发之后
router.afterEach(to, from) 全局后置守卫,该守卫路由已经离开时触发,该守卫没有next, next 函数也不会改变导航本身
到此这篇关于Vue-Router的routes配置详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Vue-Router routes配置内容请搜索NICE源码以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持NICE源码!









