本文实例讲述了PHP命名空间用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
在讲解命名空间之前,我们先了解一个问题。
我们在网站根目录创建一个文件夹,在文件夹中创建a.php
<?php
class Apple{
function get_into(){
echo "this is A";
}
}
然后再创建一个b.php
<?php
class Apple{
function get_into(){
echo "this is B";
}
}
再创建一个index.php,并且想要在index.php中同时使用a.php和b.php中的Apple类,所以我们用require_once进行引用
<?php require_once "a.php"; require_once "b.php";
此时我们在浏览器中运行index.php,就会看到一行错误信息。Cannot redeclare class Apple,意思是我们不能重写Apple类。
而如果我们确实需要同时用到时,这时候就可以运用到命名空间解决这个问题。将a.php和b.php稍微更改:
a.php
<?php
namespace a\b\c;
class Apple{
function get_into(){
echo "this is A";
}
}
b.php
<?php
namespace d\e\f;
class Apple{
function get_into(){
echo "this is A";
}
}
这时我们重新刷新index.php,可以看到已经没有报错了,因为这两个Apple类在不同的命名空间中,不存在重写问题了。
我们分别实例化a.php和b.php中的两个类,分别调用其中的get_info方法。
<?php require_once "a.php"; require_once "b.php"; $a = new \a\b\c\Apple(); $a->get_into(); $b = new \d\e\f\Apple(); $b->get_into();
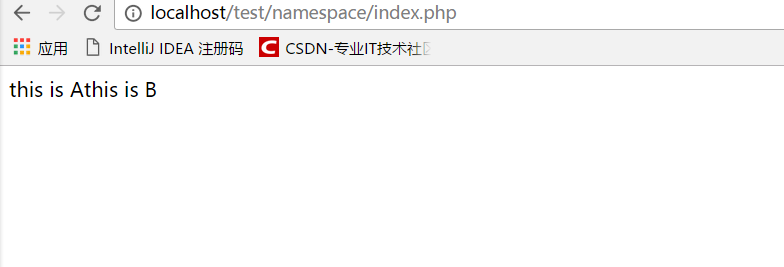
刷新之后可以看到我们成功地调用了两个类中的方法。那么问题又来了,如果我们需要多次实例化这个类,岂不是每次都要一长串的命名空间?这样看起来代码十分臃肿。我们可以对代码再做修改。
<?php require_once "a.php"; require_once "b.php"; use \a\b\c\Apple; use d\e\f\Apple as Bapple; $a = new Apple(); $a->get_into(); $b = new Bapple(); $b->get_into();
在代码中我们使用了use来使用命名空间,但是如果继续使用use \d\e\f\Apple显然和上面一行代码产生了冲突,我们可以使用as对\d\e\f中的Apple设置一个别名,这个时候$b = new Bapple();就不会产生二义性了。
在浏览器中运行index.php,可以看到输出的结果就是我们预期的结果。
更多关于PHP相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题